FIGURE 1.
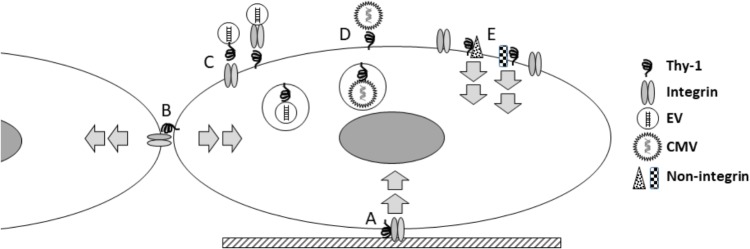
Thy-1 integrates diverse extracellular signals. Thy-1 has been known to participate, via interaction with integrins, in transducing signals from the extracellular matrix (A); more recently this understanding has expanded to include mechanical signals. This type of signaling involves Thy-1 interacting in cis with other molecules within the same cell membrane. Thy-1 is also known to interact in trans with molecules in other cells, in mediating cell-cell interactions (B), with signaling effects in both cells. More recently, Thy-1 has been shown to facilitate binding and internalization of extracellular vesicles (EV; C) and cytomegalovirus (CMV; D). Increasingly, Thy-1 has been shown to interact with a growing number of non-integrin signaling partners (E). Because the signaling associated with Thy-1 regulates many fundamental cellular processes (stemness, differentiation, migration, and survival), ongoing studies to better understand the molecular mechanisms involved will continue to yield important biological insights about how cells integrate extracellular information.