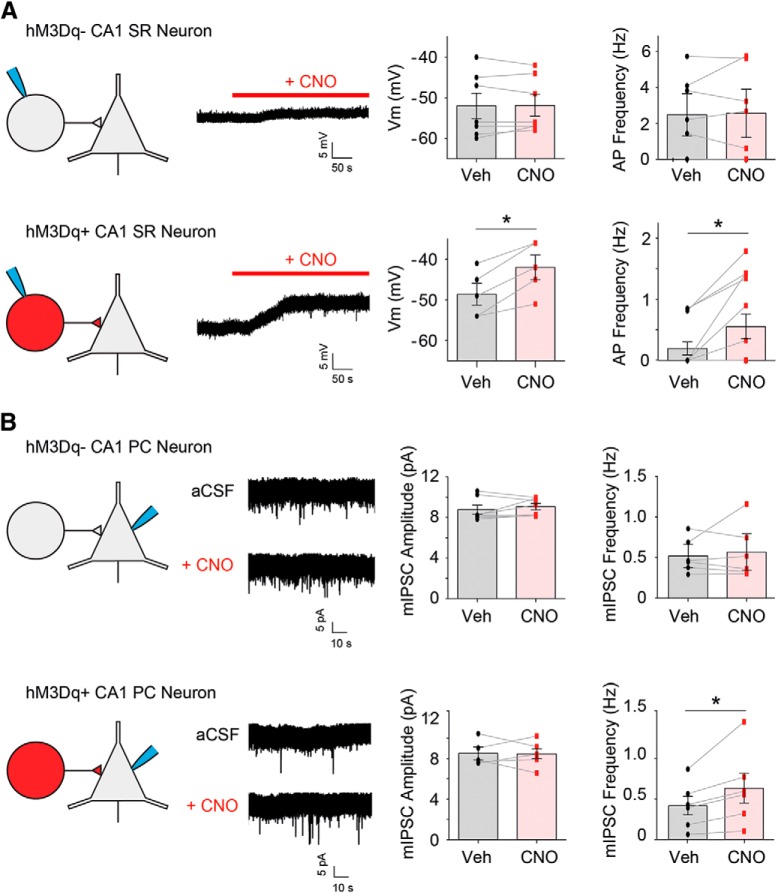
Figure 2.
Selective activation of CCK-GABA neurons increases inhibition of CA1 pyramidal neurons in CCK-GABA/hM3Dq mice. A, Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings of CA1 SR neurons in CCK-GABA/hM3Dq- (top) and CCK-GABA/hM3Dq+ mice (bottom) with and without CNO. In SR neurons from CCK-GABA/hM3Dq+ mice only, the administration of CNO (5 µM) significantly depolarized the membrane potential (n = 5) and increased firing rate (n = 13). B, Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal cells (PCs) in CCK-GABA/hM3Dq- (top) and CCK-GABA/hM3Dq+ mice (bottom) with and without CNO. In CA1 PC neurons from CCK-GABA/hM3Dq+ only (n = 6), CNO increased the frequency but not amplitude of mIPSCs. All figures present data as mean ± SEM. The asterisk indicates statistical significance at the p < 0.05 level.