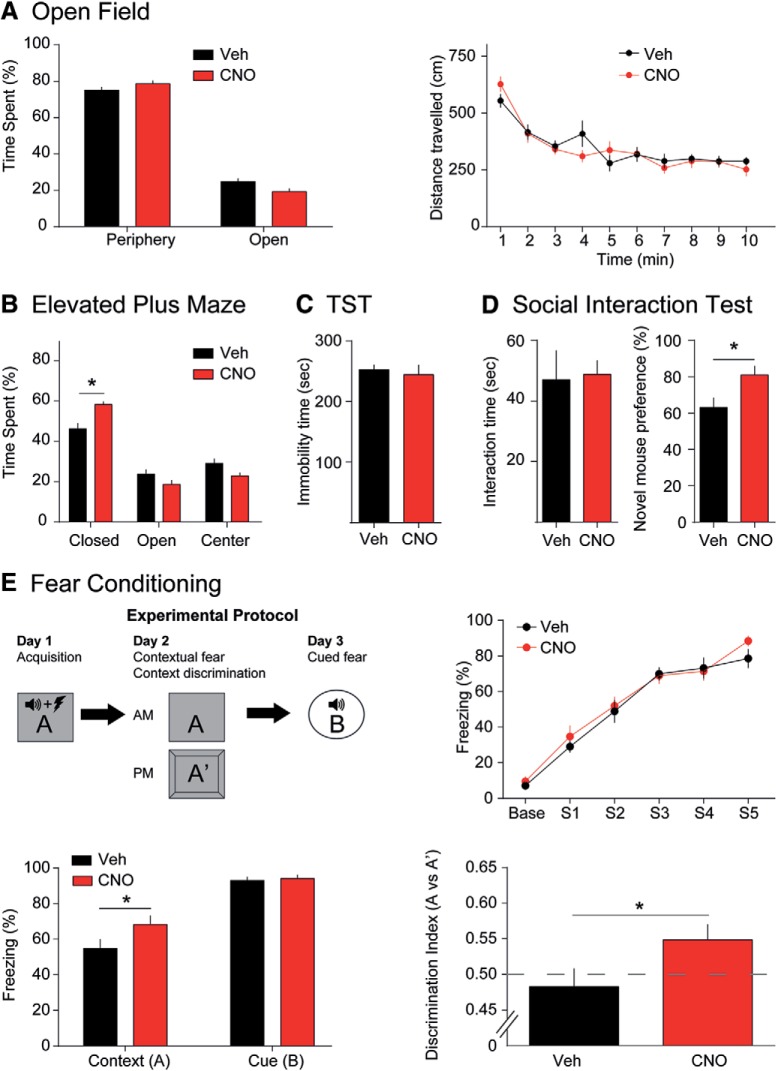
Figure 3.
CCK-GABA neuron activation minimally affects overall emotional behavior but enhances contextual fear memory. A, OF test. CNO-treated mice (red, n = 10) do not differ from vehicle-treated mice (black, n = 9) in center time, periphery time, or distance traveled. B, EPM. CNO-treated mice (n = 13) show significantly higher closed arm time than vehicle-treated controls (n = 14). However, open and center arm time was not significantly different between groups. C, TS test. Immobility time, an indicator of behavioral despair and depression-like behavior, does not differ between vehicle-treated (n = 6) and CNO-treated animals (n = 7). D, Social interaction test. Preference for novel mice, an indicator of social recognition, is higher in CNO-treated animals (n = 10) than vehicle controls (n = 10). Interaction time is unaffected by CNO. E, Fear conditioning and contextual discrimination. Top, left, Experimental protocol. Top, right, CNO-treated (n = 13) and vehicle-treated (n = 11) animals show similar responses during training sessions. Bottom, left, Recall of contextual but not cued fear conditioning, as evidenced by percentage freezing, is significantly greater in CNO-treated mice. Bottom, right, CNO-treated mice show greater contextual discrimination than vehicle-treated mice. All figures present data as mean ± SEM. Behavioral data in hM3Dq- mice is given in Extended Data Figure 3-1. The asterisk indicates statistical significance at the p < 0.05 level.