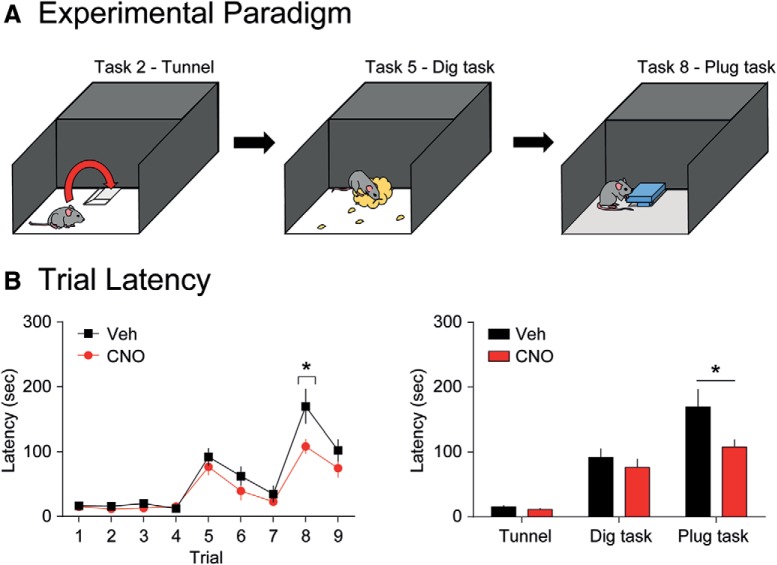
Figure 5.
Selective activation of CCK-GABA neurons enhances performance in the puzzle box test. A, Cartoon of the puzzle box test showing all trials in which a new obstacle is introduced (trial 2: underpass; trial 5: dig; trial 8: plug). In these trials, the mouse must acquire a new strategy to escape from the start area into the goal area. B, left, Escape latency of CNO- (n = 11) and vehicle-treated (n = 14) CCK-GABA/hM3Dq mice in all nine trials of the puzzle box test. Lower escape latencies indicate better performance. CNO-treated mice show significantly lower escape latency only in trial 8 (plug task). B, right, Escape latencies for CNO-treated and Veh-treated mice in all novel obstacle trials (underpass, dig, and plug task). All figures present data as mean ± SEM. Behavioral data in hM3Dq- mice is given in Extended Data Figure 3-1. The asterisk indicates statistical significance at the p < 0.05 level.