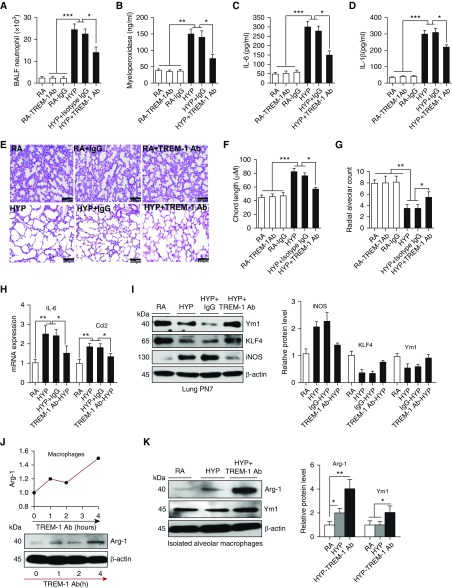
Figure 3.
TREM-1 activation decreased pulmonary alveolar injury and inflammation by polarizing macrophages toward the M2 phenotype. (A and B) Neutrophil recruitment and myeloperoxidase concentrations in the lung significantly decreased in newborn mice treated with TREM-1 agonist antibody (Ab) during HYP. TREM-1 agonist Ab and isotype Ab were given subcutaneously on alternate days starting at PN2. (C and D) ELISA for IL-6 and IL-1β in lung homogenates from mice treated with TREM-1 agonist Ab and isotype Ab. (E–G) Chord length and radial alveolar count in neonatal mice treated with TREM-1 agonist Ab and isotype Ab during HYP exposure. Measurements were taken at ×10 magnification. Scale bars: 200 μm. (H and I) TREM-1 augmentation decreased M1 markers (IL-6, inducible nitric oxide synthase [iNOS], Ccl2) and increased concentrations of M2 markers (Ym1 and KLF-4) in the lungs of HYP-exposed newborn mice. (J) Macrophages treated with TREM-1 agonist Ab polarized macrophages to the M2 phenotype in a time-dependent manner. (K) Alveolar macrophages (AM) exposed to HYP and treated with TREM-1 agonist Ab polarized macrophages to the M2 phenotype. All the data are expressed as mean ± SEM with n = 10–12 animals per group. For AM experiments, AM were pooled together from three mice and repeated twice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by Student’s unpaired t test and one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Arg-1 = arginine 1.