Figure 10.
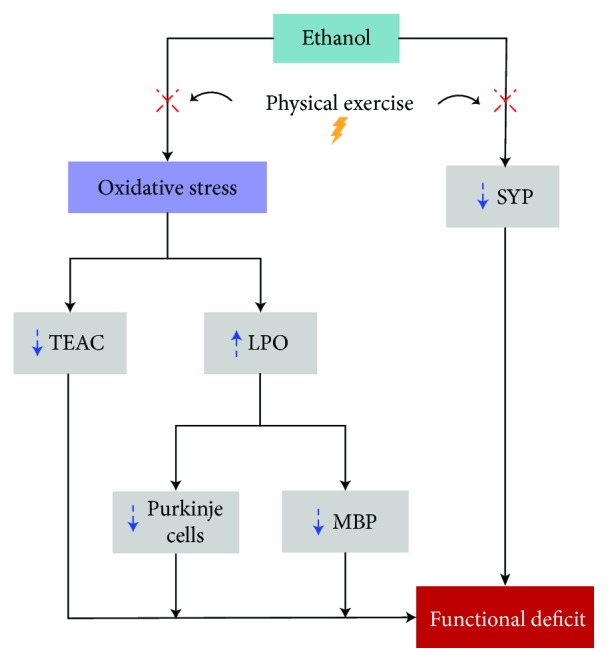
Description of the main results found in this article. Exposure to binge-like ethanol caused lower antisynaptophysin (SYP) immunostaining and oxidative stress, from the decrease of Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) levels and higher lipid peroxidation (LPO). The oxidative biochemistry misbalance induced tissue damages, as decrease of Purkinje cell population and antimyelin basic protein (MBP) immunostaining. The oxidative biochemistry and tissue damage were the main factors responsible for fine motor control changes. In addition, we indicated the role of physical exercise in damage ways in exposure to binge-like ethanol.
