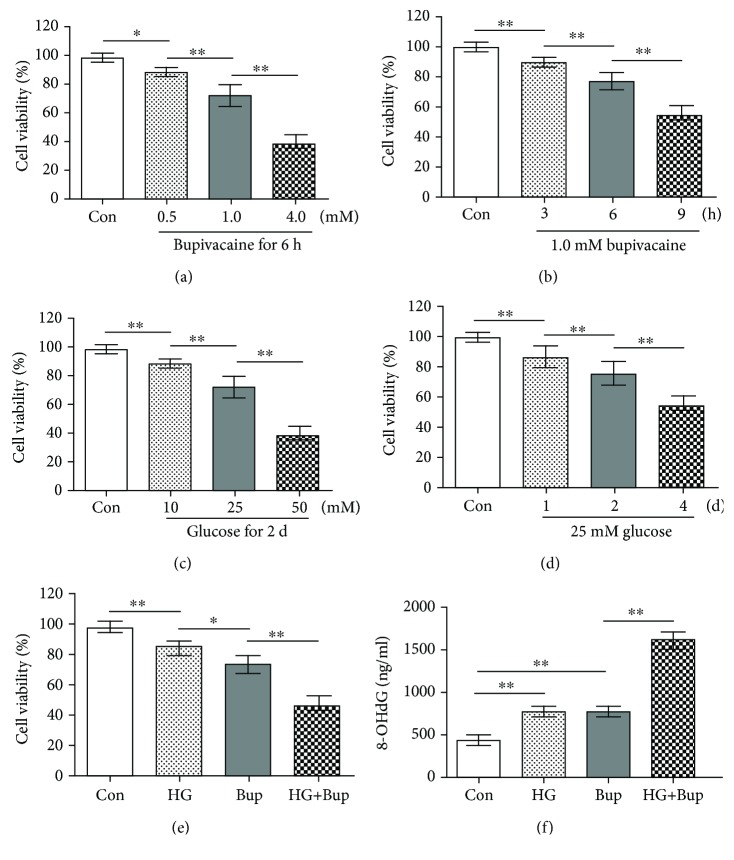
Figure 1.
High glucose enhanced bupivacaine-induced cell viability inhibition and oxidative damage in SH-SY5Y cells. Con: untreated cells; HG: cells treated with 25 mM glucose for 2 days; Bup: cells treated with 1.0 mM bupivacaine for 6 h; HG+Bup: cells cultured with 25 mM glucose for 2 days and treated with 1.0 mM bupivacaine for 6 h. (a) Cell viability was measured with MTT assay in cells treated with different concentrations (0.5, 1.0, or 4.0 mM) of bupivacaine for 6 h. (b) Cell viability was measured with MTT assay in cells treated with 1.0 mM bupivacaine for different times (3, 6, or 12 h). (c) Cell viability was measured with MTT assay in cells treated with different concentrations (10, 25, or 50 mM) of glucose for 2 days. (d) Cell viability was measured with MTT assay in cells treated with 25 mM glucose for different times (1, 2, or 4 days). (e) Cell viability was measured with MTT assay in cells cultured with 25 mM glucose for 2 days and treated with 1.0 mM bupivacaine for 6 h. (f) The 8-OHdG level was measured with ELISA in cells cultured with 25 mM glucose for 2 days and treated with 1.0 mM bupivacaine for 6 h. Values are the mean ± SD (n = 6); ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01.