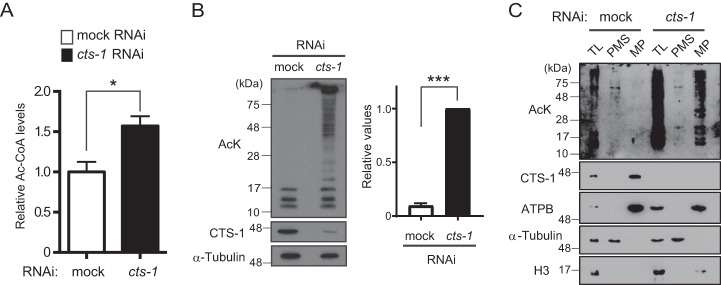
Figure 3.
cts-1 knockdown causes an increase in acetyl-CoA levels and mitochondrial protein hyperacetylation in early embryos. A, the levels of acetyl-CoA in mock and cts-1 RNAi embryos with LC-MS/MS. Data are mean ± S.E.; n = 3; *, p < 0.05. B, left, acetylated proteins of mock RNAi embryos and cts-1 RNAi embryos (AcK, acetylated proteins; CTS-1, citrate synthase-1). Right, the levels of total acetylated proteins larger than 28 kDa in mock and cts-1 RNAi embryos (data are mean ± S.E.; n = 3; ***, p < 0.001). C, acetylated proteins of total lysate (TL), post-mitochondrial supernatant (PMS), or mitochondrial pellets (MP) in mock and cts-1 RNAi embryos (ATPB, ATP synthase β; Η3, histone H3).