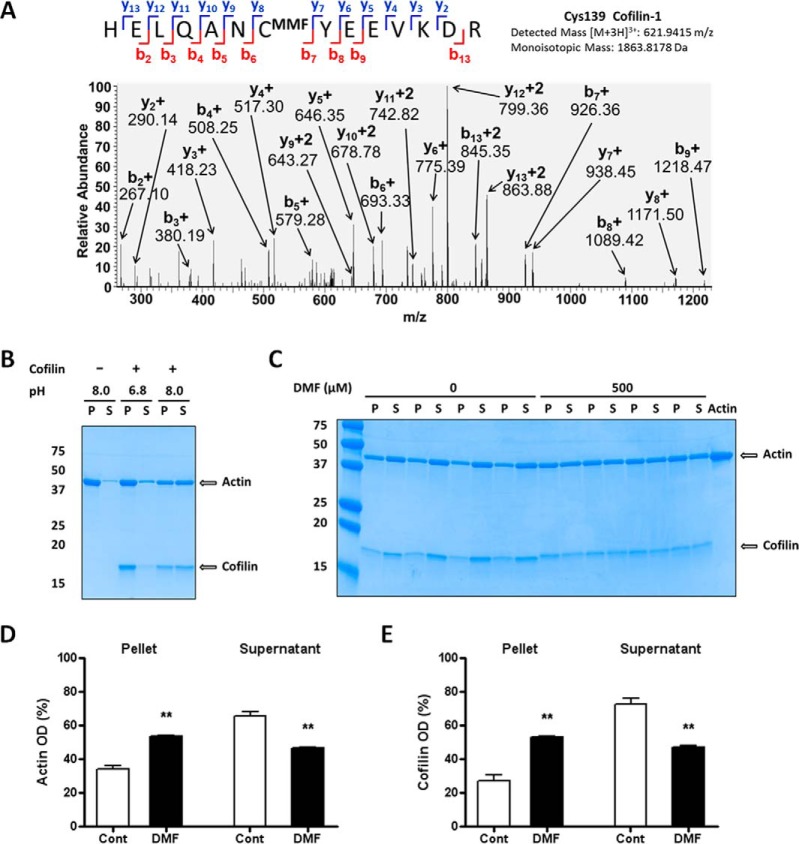
Fig. 2.
Modification of cofilin impairs the depolymerization of actin filaments. A, MS/MS spectrum from astrocyte protein extracts after DMF treatment showing the MMF succinated Cys139 of cofilin 1 in the peptide HELQANCMMFYEEVKD. B, Confirmation that the cofilin severing effect on F-actin is pH-dependent. Samples of cofilin (7.5 μg, lanes 3–6) were incubated with F-actin (15 μg) in a buffer at pH 6.8 (lanes 3–4) or 8.0 (lanes 5–6); tubes containing actin only at pH 8.0 (lanes 1–2) were included as negative controls. After centrifugation, SDS/PAGE separation and Coomassie blue staining, the distribution of actin and cofilin was studied in the pellet after centrifugation (P) and the supernatant (S). Only the mix incubated at pH 8.0 showed cofilin severing activity on F-actin (lanes 5–6, note that the distribution of actin and cofilin is similar in P and S fractions); cofilin was inactive at pH 6.8 (lanes 3–4). C, Succination by DMF reduces cofilin severing effect on F-actin. Samples of cofilin (7.5 μg) were incubated with vehicle (0, lanes 1–8) or 500 μm DMF (500, lanes 9–16) and added to tubes containing F-actin (15 μg, lanes 1–17; lane 17 contained only actin as a negative control), and samples were processed as in (B). D and E, Quantification of the bands in (C), showing that exposure of cofilin to DMF decreases cofilin severing activity on F-actin. Results were expressed as mean ± S.E., with n = 4, ** p < 0.01 versus control (no DMF) by unpaired Student's t test.