Fig. 2.
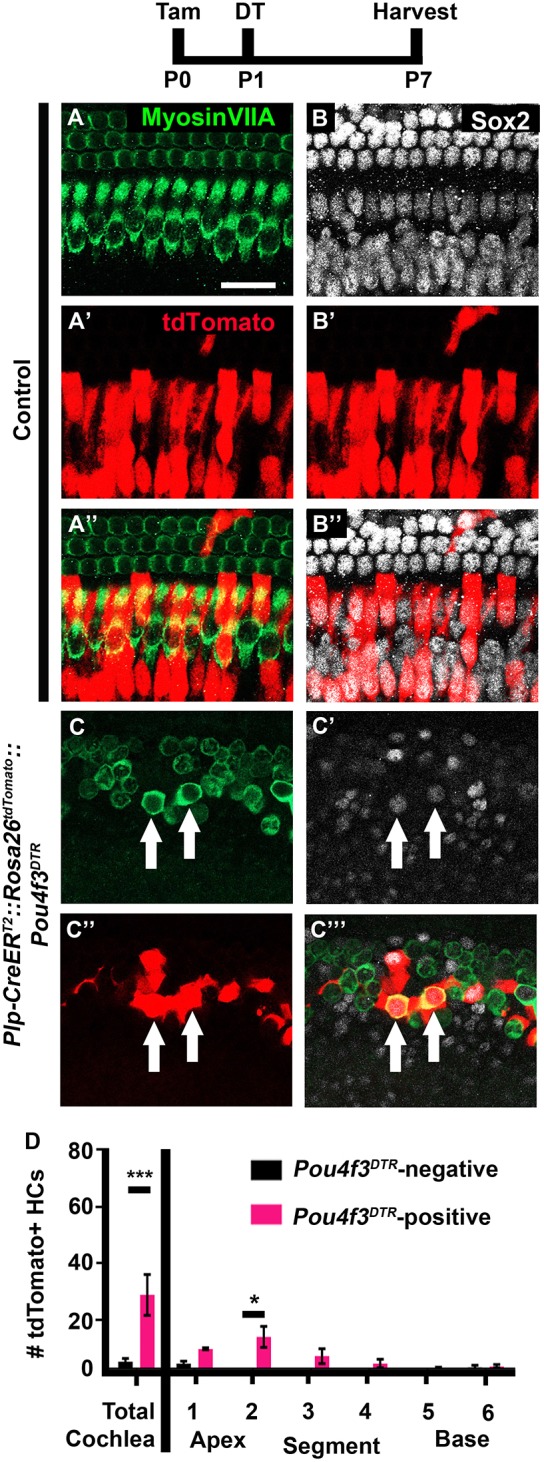
IPhCs and BCs spontaneously regenerate HCs in the neonatal mouse cochlea. (A-C‴) Representative confocal slice images from P7 Plp-CreERT2::Rosa26tdTomato::Pou4f3DTR mice (C-C‴), as well as littermate controls that lacked Pou4f3DTR (A-B″). All mice were injected with tamoxifen (Tam) at P0 to induce tdTomato expression in IPhCs/BCs and with diphtheria toxin (DT) at P1 to induce HC death in the experimental samples. Anti-myosin VIIa antibodies were used to label HCs (green); anti-Sox2 antibodies were used to label SC and immature HC nuclei (white); tdTomato was detected using endogenous fluorescence (red). Arrows indicate tdTomato-positive, regenerated HCs. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Quantification of fate-mapped HCs in the six segments of the cochlea show that more tdTomato-positive HCs were detected after HC damage compared with Pou4f3DTR-negative controls. ***P<0.001, determined using a Student's t-test (for total cochlea); *P<0.05, determined using a two-way ANOVA with a Sidak's post-hoc test (for the six segments). Data are mean±s.e.m.; n=4.
