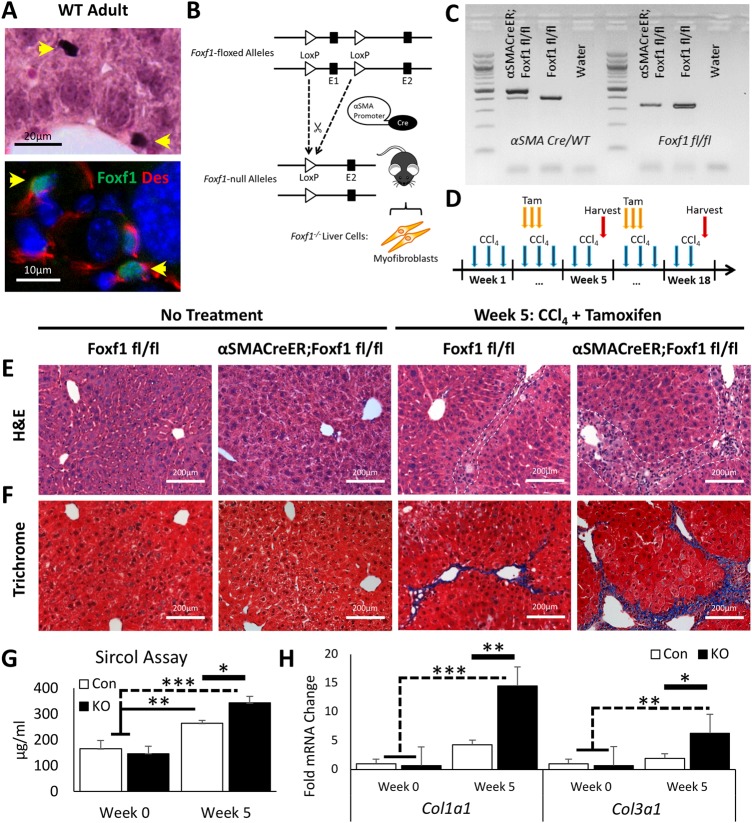
Fig. 1.
Hepatic fibrosis is increased after CCl4 injury in mice with FOXF1 deficiency. (A) FOXF1 co-localizes with DES in hepatic stellate cells in adult mice. (B) Diagram demonstrates αSMA-CreER transgene with LoxP sites flanking the Foxf1 Exon 1 (encoding DNA-binding domain). (C) DNA gel shows genotypes of Foxf1fl/fl and αSMACreER;Foxf1fl/fl mice. (D) Diagram illustrates CCl4 and tamoxifen (Tam) treatment protocol. (E,F) H&E and Masson's trichrome staining show fibrotic depositions after five weeks of CCl4 treatment. Fibrosis was increased in livers from αSMACreER;Foxf1−/− mice. White dashed lines indicate fibrotic lesion boundaries. (G) Collagen deposition was quantitated using the Sircol assay. n=2 mice per group in week 0; n=4 mice per group in week 5. (H) qRT-PCR analysis demonstrates significant increases in Col1α1 and Col3α1 mRNAs in livers from αSMACreER;Foxf1−/− mice. n=3 mice per group in week 0; n=5 mice per group in week 5. Untreated livers from Foxf1fl/fl and αSMACreER;Foxf1fl/fl mice were used as normal controls. mRNAs were normalized to Actb. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.