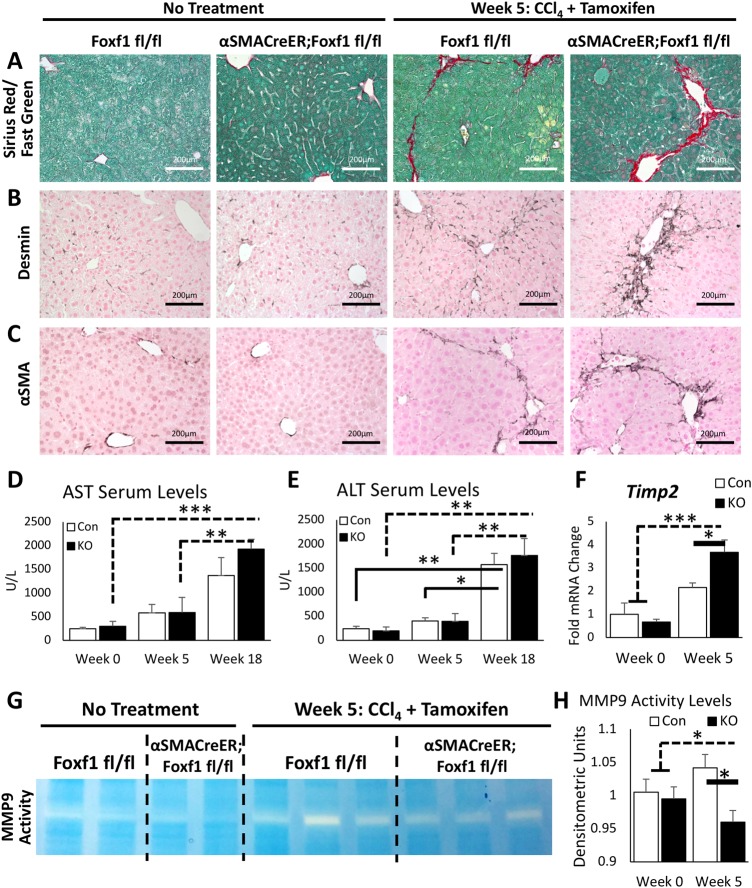
Fig. 3.
Deletion of Foxf1 from myofibroblasts increases liver fibrosis and inhibits MMP9 activity. (A) Sirius Red/Fast Green staining demonstrates increased collagen deposition between portal triads in CCl4-treated αSMACreER;Foxf1−/− livers. (B,C) Immunohistochemistry shows increased staining for DES and αSMA in CCl4-treated αSMACreER;Foxf1−/− livers. (D,E) Serum enzymatic analysis demonstrates increased AST and ALT levels after chronic CCl4-induced liver injury. Foxf1 deletion does not affect AST or ALT in blood serum. For AST levels: n=3 control mice and n=4 KO mice in week 0; n=5 control mice and n=5 KO mice in week 5; n=4 control mice and n=7 KO mice in week 18. For ALT levels: n=5 control mice and n=6 KO mice in week 0; n=7 control mice and n=8 KO mice in week 5; n=4 control mice and n=7 KO mice in week 18. (F) Increased Timp2 mRNA in CCl4-treated αSMACreER;Foxf1−/− livers is found by qRT-PCR. (G) Representative zymography gel shows decreased MMP9 activity in CCl4-treated αSMACreER;Foxf1−/− livers. Cropped gel is presented here with full gel presented in Fig. S12. (H) Quantification of zymography gels reveals a significant decrease in MMP9 activity in CCl4-treated αSMACreER;Foxf1−/− livers. Quantification was averaged across three gels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.