Fig. 2.
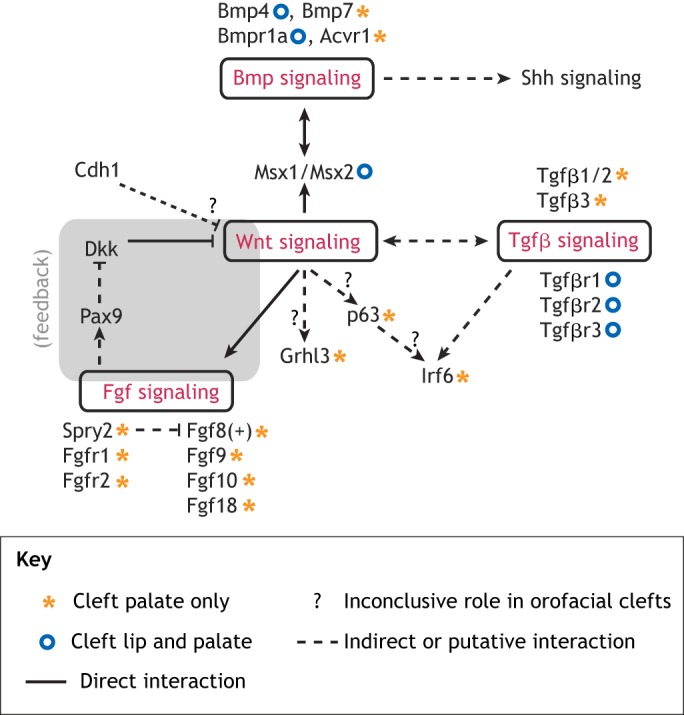
Crosstalk between Wnt, Cdh1, Bmp, Tgfβ and Fgf signaling pathways in orofacial clefts. In lip and palate primordia, the cell adhesion molecule Cdh1 may negatively regulate canonical Wnt signaling, which may interact with Bmp signaling through the common targets Msx1/Msx2. Wnt signaling also regulates Tgfβ signaling in palatogenesis. Tgfβ signaling modulates the orofacial cleft-causing gene Irf6, which may also be regulated by Wnt signaling through p63. Moreover, Wnt signaling can activate Fgf signaling, which modulates Pax9 to repress Dkk protein, an inhibitory ligand of Lrp6 in the canonical Wnt pathway, forming a positive-feedback regulatory loop during orofacial development. The Spry protein family is known to inhibit Fgf signaling. Grhl3 and Irf6 are well-known candidates for Van der Woude syndrome, a syndromic form of CLP. However, their regulation by Wnt has yet to be elucidated. The phenotypic outcomes of the key signaling components, demonstrated in mutant mouse models, are marked as per the figure key.
