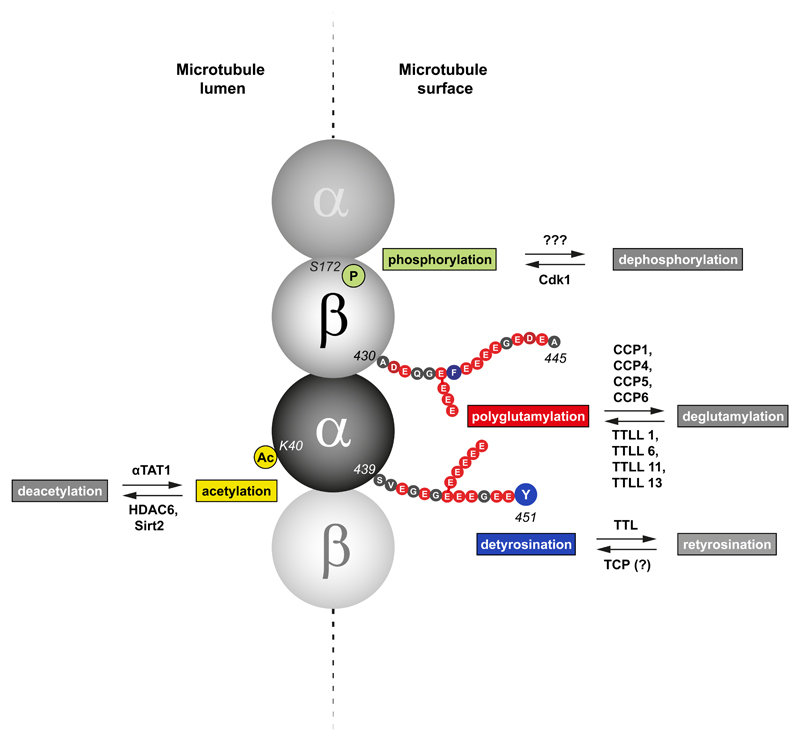
Figure 2. Tubulin PTMs with potential roles in mitosis.
Illustrative model depicting different post-translational modifications of the tubulin dimers within a microtubule (modified from ref. (7)) with potential roles during mitosis. Acetylation of lysine 40 of α–tubulin occurs on the microtubule lumen and is mediated by the tubulin acetyl transferase αTAT1, whereas deacetylation is performed by at least two deacetylases, HDAC6 and Sirt2. Detyrosination of α–tubulin and polyglutamylation of both α– and β–tubulin take place at the outer surface of the microtubule lattice, which is in direct contact with motor proteins. Tubulin detyrosination is driven by a yet-unidentified tubulin carboxypeptidase (TCP), while retyrosination requires action of the tubulin tyrosine ligase (TTL). Polyglutamylation is catalyzed by multiple TTL-like (TTLL) glutamylases and reversed by several deglutamylases. Phosphorylation of Ser172 of β-tubulin occurs specifically during mitosis and is mediated by Cdk1 kinase.