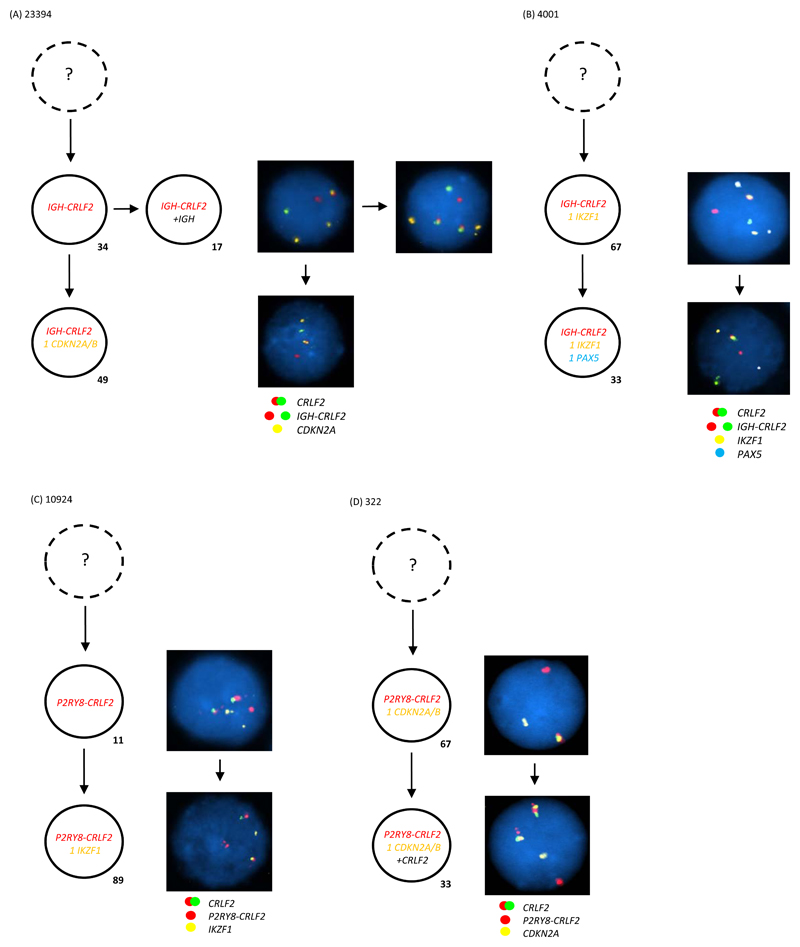
Figure 1. Multiple colour FISH showing examples of IGH-CRLF2 as a clonal event arising (A) first or (B) together with other tracked abnormalities (C) P2RY8-CRLF2 as a clonal event arising first or (D) together with other tracked abnormalities.
- Representative FISH images on the right show examples of each leukaemic sub-clone.
- Leukaemic sub-clone percentages for the diagnostic samples are indicated next to each clone and only include populations above the 8% cut off.
- Dotted clone with “?”: presumed but undetected founder clone.
(A) For patient 23394 a total of 245 abnormal nuclei at diagnosis were scored for probes to CRLF2 (red/green) and CDKN2A/B (gold). In 34% of nuclei the IGH-CRLF2 translocations was an early event observed in the presence of two copies of CDKN2A/B. This clone evolves into two sub-clones: one gains an extra copy of IGH in 17% of nuclei; one loses a single copy of CDKN2A/B in 49% of nuclei.
(B) For patient 4001 a total of 129 abnormal nuclei at diagnosis were scored for probes to CRLF2 (red/green), IKZF1 (gold) and PAX5 (aqua). In 67% of nuclei the IGH-CRLF2 translocation was present with one copy of IKZF1 and two copies of PAX5. This clone evolves with loss of a single copy of PAX5 in 33% of nuclei.
(C) For patient 10924 a total of 227 abnormal nuclei at diagnosis were scored for probes to CRLF2 (red/green) and IKZF1 (gold). In 11% of nuclei the P2RY8-CRLF2 fusion is an early event before the loss of a single copy of IKZF1 observed in the bulk leukaemic clone at 89%.
(D) For patient 322 a total of 70 abnormal nuclei at diagnosis were scored for probes to CRLF2 (red/green) and CDKN2A/B (gold). In 67% of nuclei the P2RY8-CRLF2 fusion and loss of a single copy of CDKN2A/B present together. A further 33% of cells gained an additional copy of the CRLF2 probe, which usually indicates the presence of an additional sex chromosome (+X/Y).