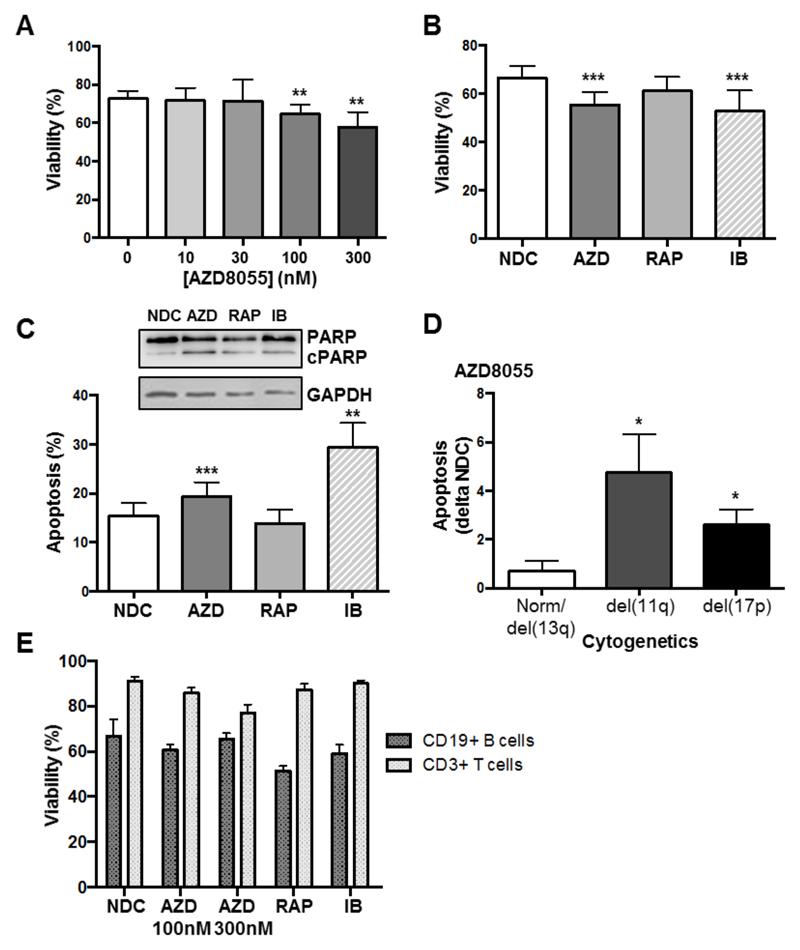
Figure 2. AZD8055 treatment selectively and significantly reduces primary CLL cell viability preferentially in poor prognostic subsets.
A. Primary CLL cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of AZD8055 or left untreated for 48 h (n=12 CLL patient samples). Cell viability was analyzed by flow cytometry, with the percentage of viable cells assessed as Annexin V-7-AAD-; B. Cell viability was compared upon treatment of primary CLL cells with 100 nM AZD8055 (AZD; blue), 10 nM rapamycin (RAP; red) or 1 μM ibrutinib (IB; pink) for 48 h, compared with NDC (white), (n=15); C. The level of apoptosis (Annexin V+7-AAD-) was compared upon treatment of primary CLL cells with 100 nM AZD8055, 10 nM rapamycin or 1 μM ibrutinib for 48 h, relative to NDC. p values generated by a paired two tailed t test (n=15). Inset: Western blotting was performed to show the levels of PARP cleavage (cPARP) in primary CLL cells treated with 100 nM AZD8055, 10 nM rapamycin or 1 μM ibrutinib for 48 h, or left untreated (NDC). GAPDH is included as a loading control. D. The level of apoptosis induced in primary CLL cells treated with 100 nM AZD8055 minus background (NDC) was compared between cytogenetic subgroups: good (Norm/del(13q)) vs poor (del(11q) or (17p)). p value generated by an unpaired two tailed t test (n≥7 per subgroup). E. Freshly-isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy donors, were incubated with 100 or 300 nM AZD8055, 10 nM RAP or 1 μM IB for 48 h, compared with NDC. Cell viability of B (CD19+) and T (CD3+) populations was assessed, as indicated (n=6).