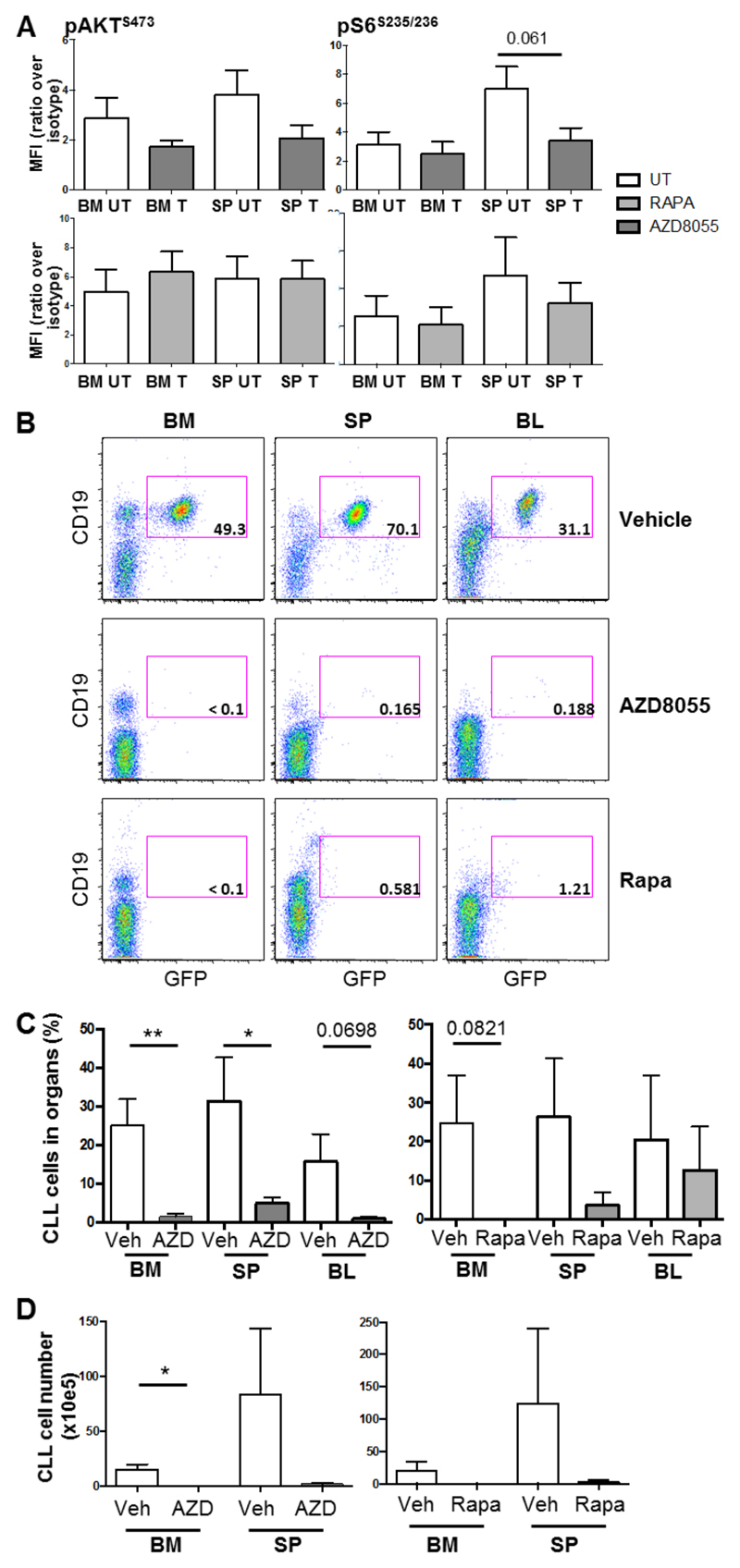
Figure 4. Treatment of leukemic mice with AZD8055 leads to a significant reduction in CLL tumor load in vivo.
A. After confirmation of a population of CLL-like cells in the blood (≥ 5% GFP+CD19+), mice were dosed with 20 mg/kg AZD8055, 4 mg/kg rapamycin or respective vehicle controls for 2 h. Thereafter, cells were isolated from BM and spleen (SP) and levels of AKTS473 and S6S235/235 phosphorylation was determined on GFP+B220+ cells with intracellular flow cytometric analysis. Data are represented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ratio of stained sample over isotype control (n=6). p value was generated using the student’s unpaired t-test. B. After confirmation of a population of CLL-like cells in the blood (≥ 0.4% GFP+CD19+), mice were dosed daily with 20 mg/kg AZD8055 (OG), 4 mg/kg rapamycin (IP) or respective vehicle control for up to 14 days. Thereafter, blood, BM and spleen were analyzed for leukemic burden. Representative flow cytometric analyses of vehicle-, AZD8055- or rapamycin-treated mice are shown. Data shown are analyzed for CLL cell markers, CD19 and GFP after live and size (FSC/SSC) and CD45+ gating. The percentage of GFP+ CLL-like cells within the total population is shown; C. Percentage and D. Number of GFP+ CD45+CD19+ cells are shown in treated mice in the organs indicated. All data shown are the mean (± SEM) of 5 individual mice. p values were generated using the student’s unpaired t-test.