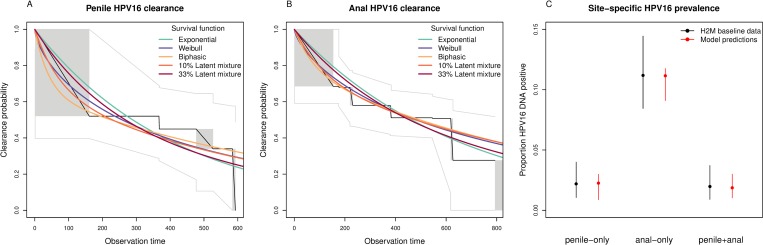
Fig 1. Outcomes of approximate maximum-likelihood fitting procedure.
This procedure consisted of separate likelihood optimization of progression and clearance parameters from event times of (A) penile and (B) anal infection clearance (time in days), and conditional estimation of remaining model parameters from multinomial likelihood optimization of (C) site-specific infection prevalence. Non-parametric survival functions (black lines; grey boxes) with 95% confidence limits (grey lines) in (A) and (B) are from a generalization of Kaplan–Meier estimates to interval-censored data [25]. Colored lines refer to various model-based survival functions fitted to interval-censored data (S3 Text). H2M baseline data in (C) are summarized as means with 95% binomial confidence intervals from 461 HIV-negative MSM. Model predictions (age-matched to H2M study participants) are given as Akaike-weighted averages with the minimum–maximum range across 360 models. HPV16, human papillomavirus genotype 16.