Figure 1. Combinatorial Screening for Forebrain Hypothalamic Neurons.
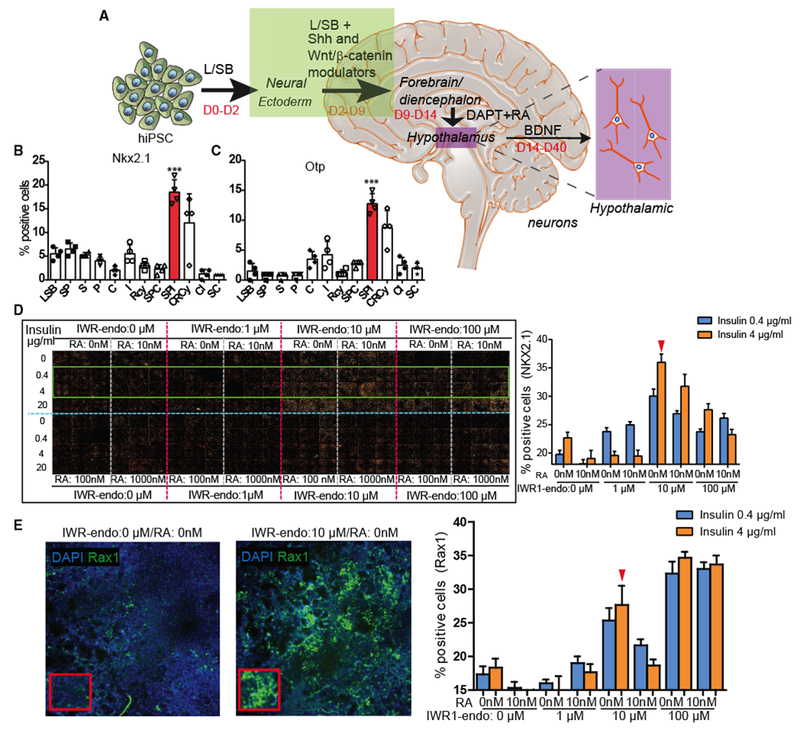
(A) A schematic of the iHTN direct differentiation protocol.
(B and C) L/SB + SPI combination showing the most (B) Nkx2.1 - and (C) Otp-positive progenitor cells. 4 independent experiments utilized 2 different cell lines and an average is represented. Small molecules utilized in (B) and (C) are as follows: L-LDN193189 (1 μM); SB, SB431542 (10 μM); S, Smoothened Agonist (1 μM); P, Purmorphamine (1 μM); I, IWR1-Endo (10 μM); RA, retinoic acid (0.01 μM); BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (10 ng/mL); C, CHIR99021 (3 μM); R, Robotnikinin (1 μM); and Cy, Cyclopamine (1 μM).
(D and E) The (D) montage and (E) image (left) and quantification (right) of large-scale combinatorial screen of varying doses of IWR1-endo, insulin, and retinoic acid (RA) in efficient differentiation of (D) Nkx2.1 + hypothalamic progenitors and (E) Rax+ hypothalamic progenitors in day 9 iHTN cultures. The green box in the montage (D) highlights the conditions represented in the bar graphs on the right. Red arrow in (D) denotes the dose combination selected for iHTN differentiation based on efficient Nkx2.1 and long-term neuropeptidergic neuron generation and cell survival. Red arrow in (E) shows that the selected combination shows efficient levels of Rax. 2 independent experiments each utilizing two cell lines were conducted and the average is represented. ***p < 0.001.
Error bars represent SEM.
