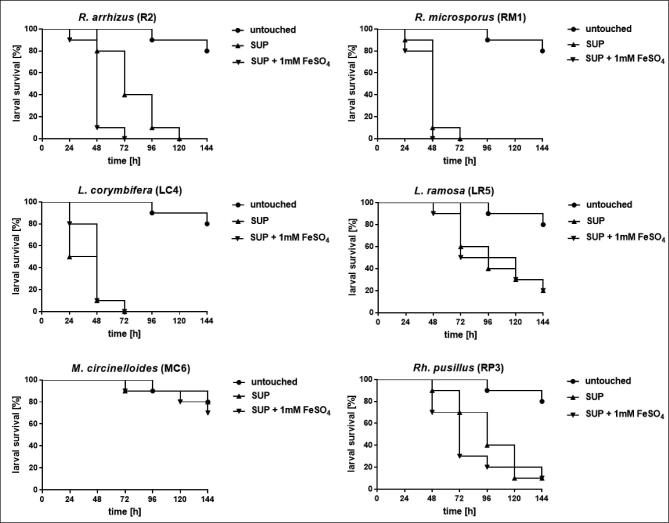
Figure 5.
Impact of iron starvation in preculture conditions on the virulence potential of human-pathogenic mucormycetes. Larvae were infected with spores that were produced by mucormycetes grown under iron starvation (SUP agar) or under high iron conditions (SUP agar supplemented with 1 mM FeSO4). In preexperiments virulence potential of each species was determined, inocula were adapted accordingly as follows: 1 × 105 for Rhizopus spp., 1 × 106 for M. circinelloides and 1 × 107 for Lichtheimia spp and Rh. pusillus. Larvae were incubated at 37°C.