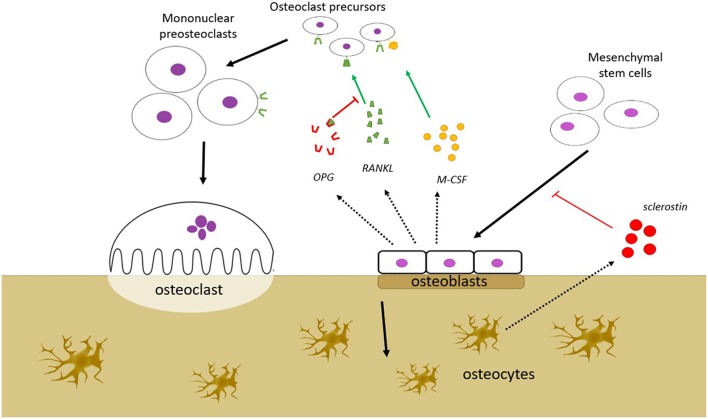
Figure 1.
Bone remodeling is a process that takes place in the bone remodeling unit (BMU). BMU consists of bone resorbing osteoclasts (OC), bone forming osteoblasts (OB), and osteocytes. The process is regulated by local signals between the cells and by external stimuli. OBs stimulate OC precursors to differentiate into mature OCs by secreting monocyte colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) and RANKL, but may also inhibit the same cells by secreting osteoprotegerin (OPG) that scavenges RANKL, preventing it from binding to the RANK receptors on the OC precursors. OBs are derived from mesenchymal stem cells, a process that is dependent on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. This pathway is inhibited by sclerostin, which is secreted from osteocytes. Several other factors which affect bone remodeling are mentioned in the text (FGF-23, BMP), but are not shown in this figure.