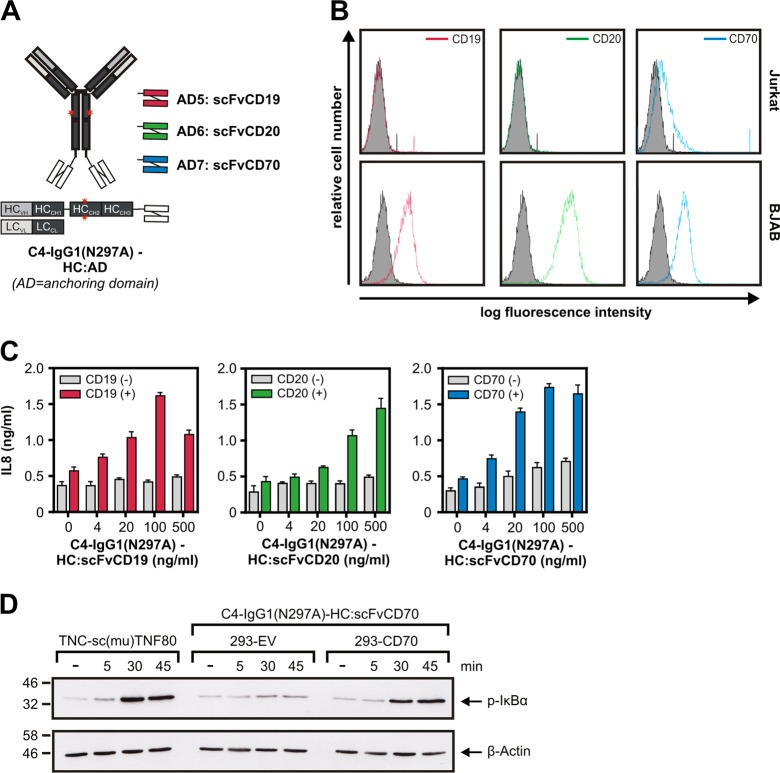
Fig. 5. C4-IgG1(N297A) scFv fusion proteins acquire high agonistic potential after binding to the scFv-targeted cell surface antigen.
a Domain architecture and structural organization of C4-IgG1(N297A)-HC:scFvCD19, C4-IgG1(N297A)-HC:scFvCD20, and C4-IgG1(N297A)- HC:scFvCD70. b Analysis of CD19, CD20, and CD70 expression of Jurkat and BJAB cells by FACS. c HeLa-TNFR2 cells and BJAB (CD19+ CD20+ CD70+) or Jurkat cells were cocultured and stimulated overnight with the indicated concentration of the various C4-IgG1(N297A) scFv fusion proteins. IL8 content of supernatants were determined by ELISA. d HeLa-TNFR2 cells alone or in combination with the indicated HEK293 transfectants were preincubated with 20 µM MLN4924 for 30 min and afterwards stimulated for the different times with C4-IgG1(N297A)-HC:scFvCD70 or TNC-sc(mu)TNF80, a potent TNFR2 agonist as a positive control. MLN4924 was used to prevent proteasomal IκBα degradation to rule out underestimation of IκBα phosphorylation. MLN4924 is an inhibitor which interferes with the activity of the E3 ligase complex responsible for K48 ubiquitination of IκBα