Figure 2.
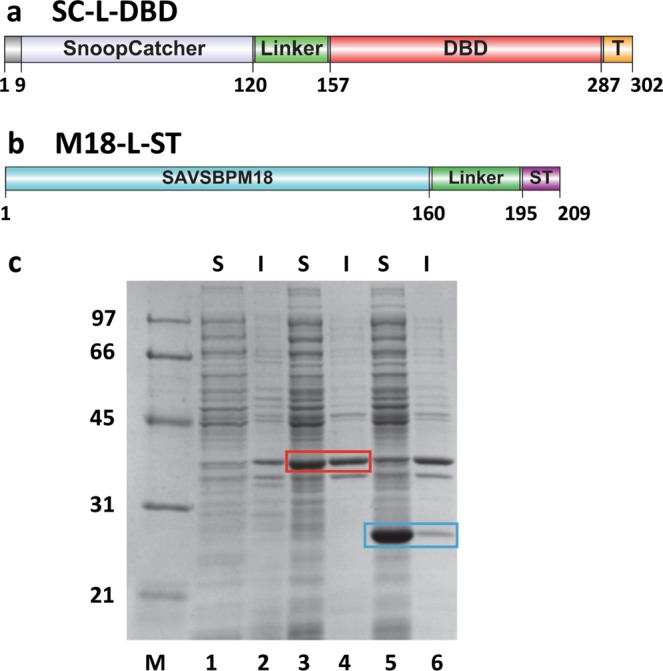
Domain organization and production of SnoopCatcher-Linker-dextran-binding domain (SC-L-DBD) and SAVSBPM18-Linker-SnoopTag (M18-L-ST). (a) A schematic drawing of various segments [a short N-terminal sequence, SnoopCatcher, linker, dextran-binding domain (DBD) and a short C-terminal tail sequence (T)] in SC-L-DBD. (b) A schematic drawing of various domains [SAVSBPM18, linker and SnoopTag (ST)] in M18-L-ST. Amino acid residues that mark the boundary of the key domains in panels a and b are listed. (c) Intracellular production of SC-L-DBD from E. coli BL21[pET29B-SC-L-DBD] and M18-L-ST from E. coli BL21[pET-29B-M18-L-ST]. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and boiled before loading to the gel. Lanes 1, 2 are the intracellular fractions from E. coli BL21 [pET29B]. These samples serve as the negative control. Lanes 3, 4 are the intracellular fractions from E. coli BL21 [pET29B-SC-L-DBD]. SC-L-DBD is boxed in red. E. coli BL21[pET29B] has an endogenous protein which comigrates at the same position as SC-L-DBD. Lanes 5, 6 are the intracellular fractions from E. coli BL21 [pET29B-M18-L-ST]. M18-L-ST is boxed in blue. M, molecular weight markers (sizes in kDa); S, soluble fraction; I, insoluble fraction.
