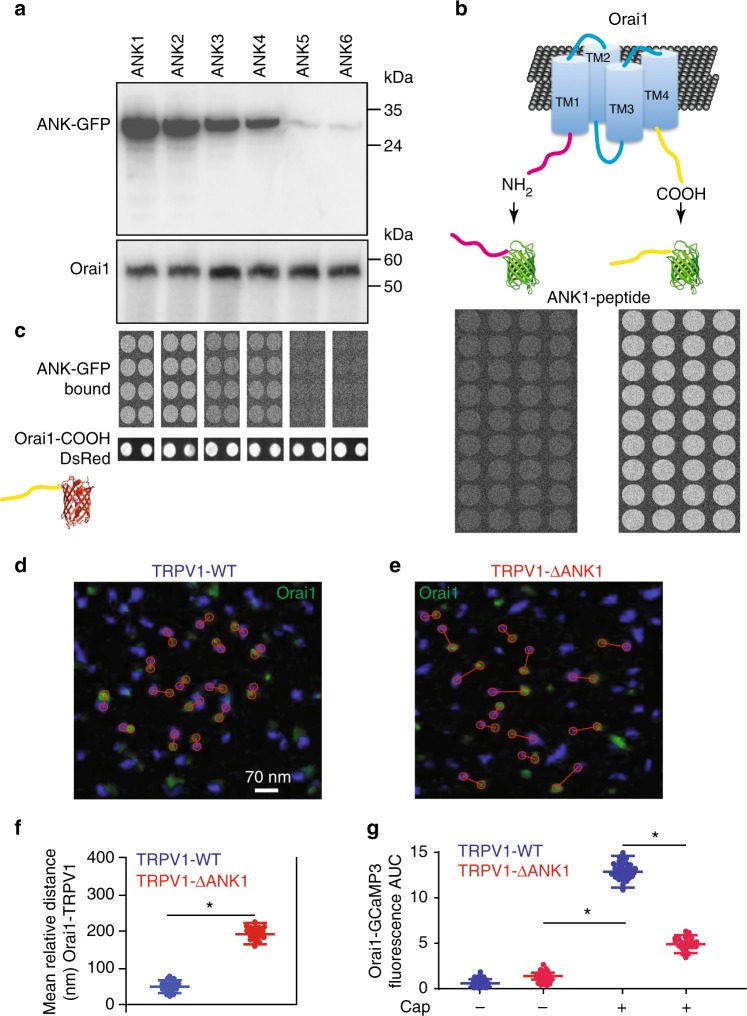
Fig. 6.
The first ankyrin domain from TRPV1 associates to the carboxyl domain from Orai1 to favor TRPV1-Orai1 association. a Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of cells expressing c-Myc-Orai1 and the 6 ankyrin domains fused to GFP (ANK1-ANK6). b Cartoon showing the fusion of the amino or the carboxyl terminus from Orai1 to GFP. Lower panels show the results of the peptide microarrays using ANK1 as bait. Notice that only COOH-GFP is captured by ANK1 but not NH2-GFP. c Peptide microarrays using the 6 ankyrin domains individually fused to GFP. In this case Orai1-COOH is used as bait (printed on the glass coverslip). Notice that Orai1-COOH retained ANK1-GFP, ANK2-GFP and less efficiently ANK3 and ANK4 but not ANK5 and ANK6. d Super resolution TIRFM images of cells expressing TRPV1 wild type (TRPV1-WT, blue) and Orai1 (green) or cells expressing TRPV1-ΔANK1 (right panel, e). Red circles show the distance between the closest pair of channels and the lines connect the pair. f Mean relative distance obtained from hundreds of individual channels for Orai1 with TRPV1-WT (blue) or TRPV1-ΔANK1 (red). Data shows the mean ± standard deviation. g Fluorescence increments reported by the Orai1-GCaMP3 sensor with and without capsaicin stimulation. Notice that the Orai1-GCaMP3 increases about half the fluorescence after capsaicin in cells expressing TRPV1-ΔANK1 (red bar) compared to the cells stimulated with capsaicin and expressing TRPV1-WT (green). This indicates that deletion of the first ANK domain results in Orai1 moving apart from TRPV1 and the Orai1-GCaMP3 sensor reporting less of the calcium that enters through the TRPV1 channel. *p < 0.01. The statistical significance was p < 0.05. Statistics was performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test