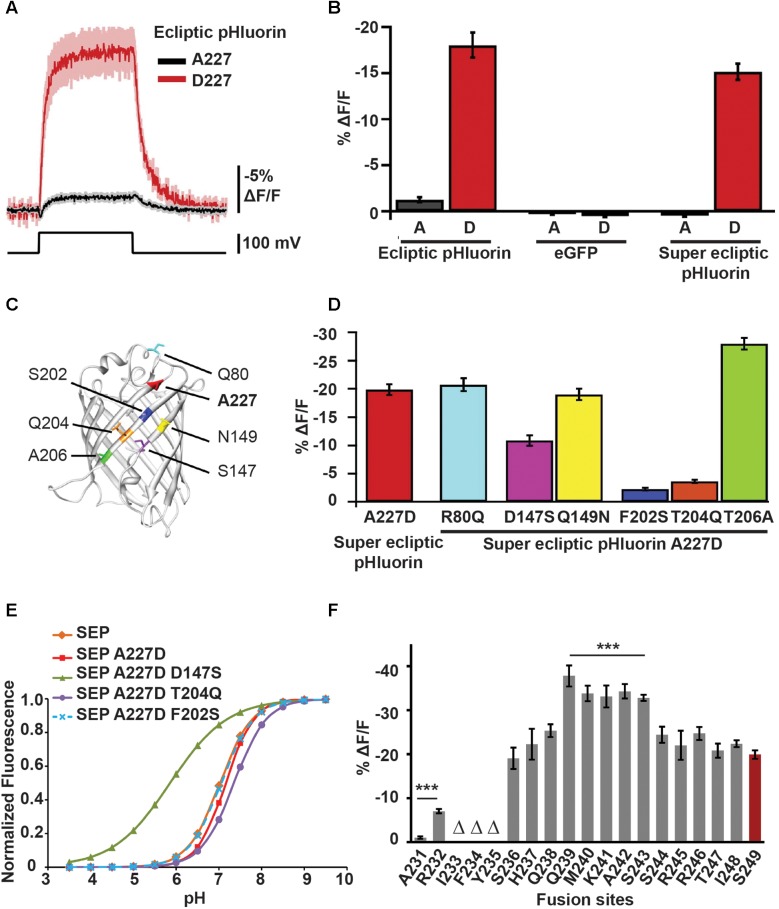
FIGURE 3.
Mutations in the FP sequence as well changes to the CiVSD-FP linker length contribute to ArcLight’s voltage sensitivity. (A) Fluorescence responses to 100 mV depolarization of HEK cells transfected with CiVSD-ecliptic pHluorin or CiVSD-ecliptic pHluorin A227D. (B) 100 mV step responses (mean ± SEM) of HEK cells expressing 227A or 227D variants of each of CiVSD-ecliptic pHluorin, CiVSD-eGFP or CiVSD-SEP. (C) Crystal structure of eGFP (PDB ID 1EMG) highlighting A227 as well as the six most dissimilar residues between SEP and eGFP. The SEP versions are indicated. Note that all four critical residues 147, 227, 202, and 204 reside on the same barrel surface of the fluorophore. (D) Fluorescence responses (mean ± SEM) of CiVSD-SEP variants harboring mutations at indicated residues in (C). These mutations serve to replace the SEP amino acids with corresponding residues found in eGFP. (E) pH sensitivity curves of SEP and SEP mutants containing eGFP residues at indicated sites. (F) Mean response amplitudes to 100 mV depolarization of ArcLight derivatives with modified linker length. Groups that significantly differ from ArcLight S249 are indicated with asterisks. Δ refers to sensors showing poor membrane localization (Jin et al., 2012; Han et al., 2014).