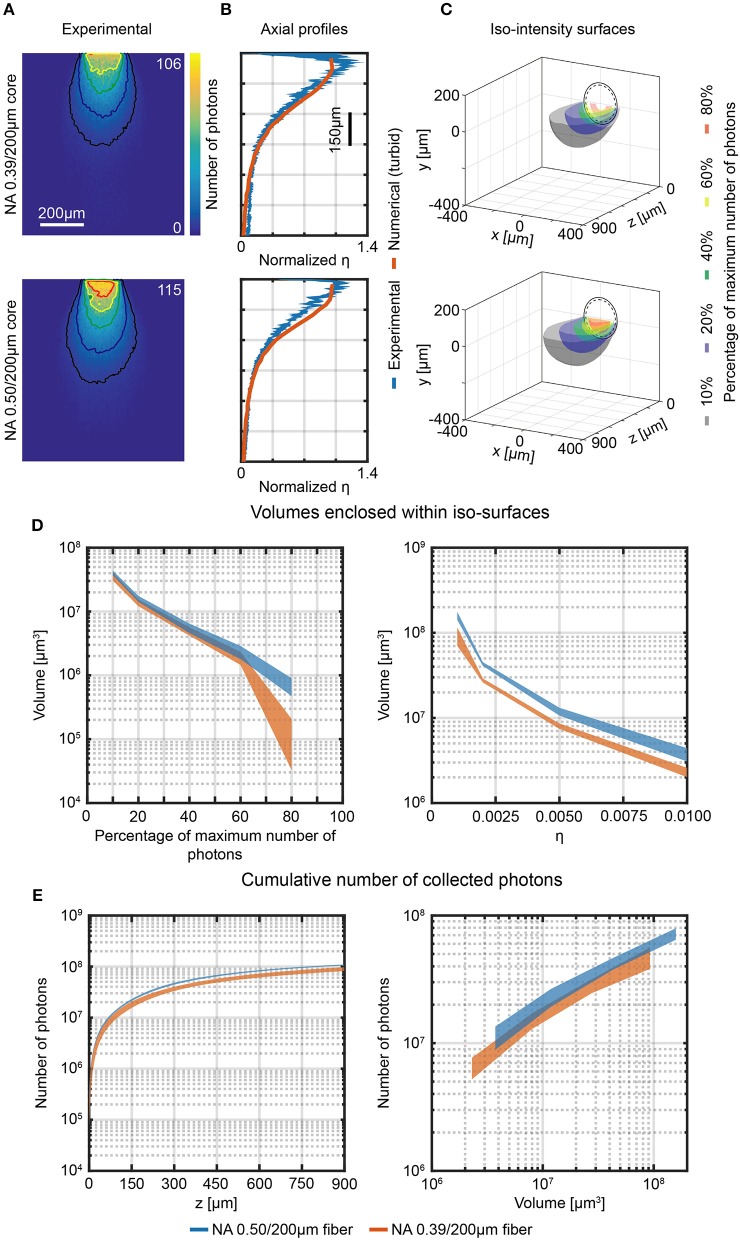
Figure 5.
Photon collection efficiency and effective collective volumes in brain slice. (A) Section y = 0 of the collection field of 0.39/200 μm and 0.50/200 μm optical fibers, measured in a 300 μm thick fluorescently stained brain slice using the 2-photon scanning system shown in Figure 3. Isolines at 10%, 20%, 40%, 60%, and 80% of the maximum number of photons are shown (in black, blue, green, yellow and red, respectively). (B) Comparison of normalized axial profiles (x = 0, y = 0) of experimental (in brain slices, blue curves) and numerical data (in turbid medium, orange curves) for 0.39/200 μm and 0.50/200 μm optical fibers. Normalization is done with respect to the average of the data points within the firsts 80 μm. The width of the blue curves represents mean ∓ standard deviation over four different fibers. (C) Cross-sections of the 3-dimensional reconstruction of the collection field of 0.39/200 μm and 0.50/200 μm fibers. Iso-intensity surfaces defining the boundaries at which the number of collected photons falls to 10%, 20%, 40%, 60%, and 80% of its maximum are shown (in black, blue, green, yellow, and red, respectively). The continuous and dashed circles represent the cladding and the core boundaries, respectively. (D) Volumes enclosed by the iso-intensity surfaces at 10%, 20%, 40%, 60%, and 80% of the maximum number of photons (left panel) and at η = 0.001, 0.002, 0.005, 0.01 (right panel) for 0.39/200 μm and 0.50/200 μm fibers (orange, and blue curves, respectively). The width of the curves represents mean ∓ standard deviation over three different fibers. (E) Cumulative number of photons collected by 0.39/200 μm and 0.50/200 μm fibers as a function of the distance from the fiber facet (left panel, number of photons are shown in a volume 900 μm × 600 μm × z) and as a function of the volume enclosed within the iso-surfaces at fixed η (right panel). The width of the curves represents mean ∓ standard deviation over three different fibers.