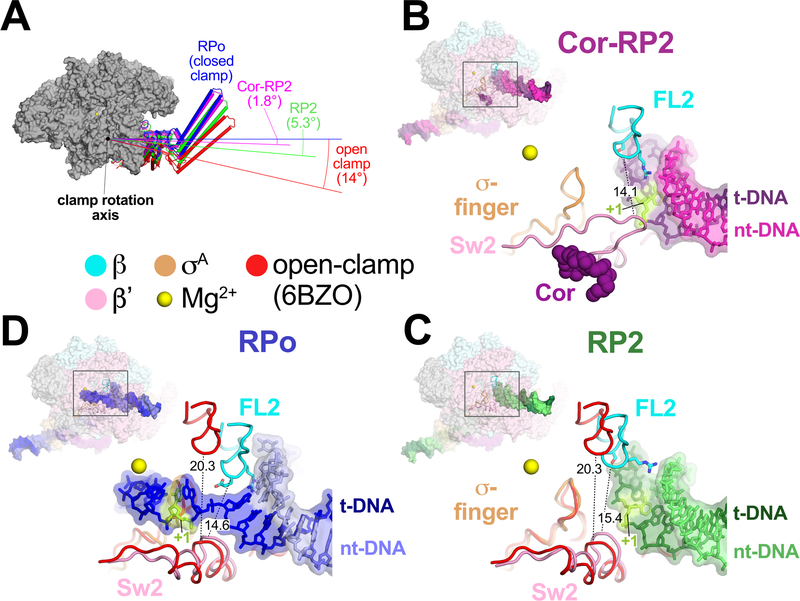
Figure 3 |. FL2, Sw2, and clamp dynamics.
A. RNAP clamp conformations. The RPo structure was used as a reference to superimpose the other structures by a common core RNAP structure (gray), revealing shifts in the clamp. Clamps are shown as cylindrical helices along with angles of clamp opening (relative to RPo at 0°). The open clamp structure (6BZO) is the Mtb RNAP bound to Fidaxomicin, which stabilizes the clamp in a fully open position without DNA in the active site cleft17.
B. Overall structure of Cor-RP2 (upper left), with the boxed region magnified (lower right) showing the DNA and RNAP structural elements colored as labeled. Side chains of FL2 residues contacting the DNA (G462, S464, R467) are shown. Cor is also shown. The shortest distance between FL2 and Sw2 α-carbons is noted.
C. Same as B but showing RP2. Superimposed are the FL2, Sw2, and σ-fingers from the open clamp structure, aligned via the clamp, modelling a transient open-clamp intermediate. The shortest distance between FL2 and Sw2 α-carbons for each structure is noted.
D. Same as C but showing RPo.