Figure 1.
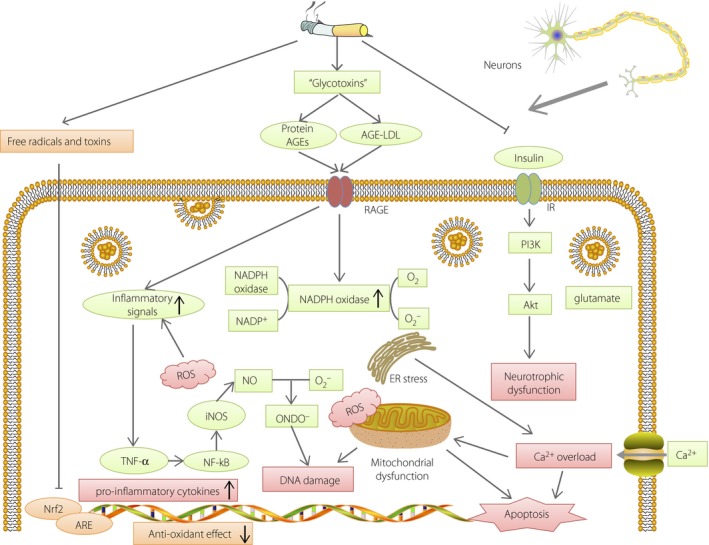
Mechanisms of cell damage in peripheral neurons caused by cigarette smoking. Cigarette smoking induces formation of advanced glycation end‐products (AGEs) and inhibits insulin signaling and the NF‐E2‐related factor 2 (Nrf2)–anti‐oxidant responsive element (ARE) pathway, causing oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage and apoptosis in peripheral neurons. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; iNOS, nitric oxide synthase; LDL, low‐density lipoprotein; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NO, nitric oxide; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end‐products; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐α.
