Figure 5. B-GelMA provides a microporous scaffold with independent stiffness and pore size for 3D cell culture.
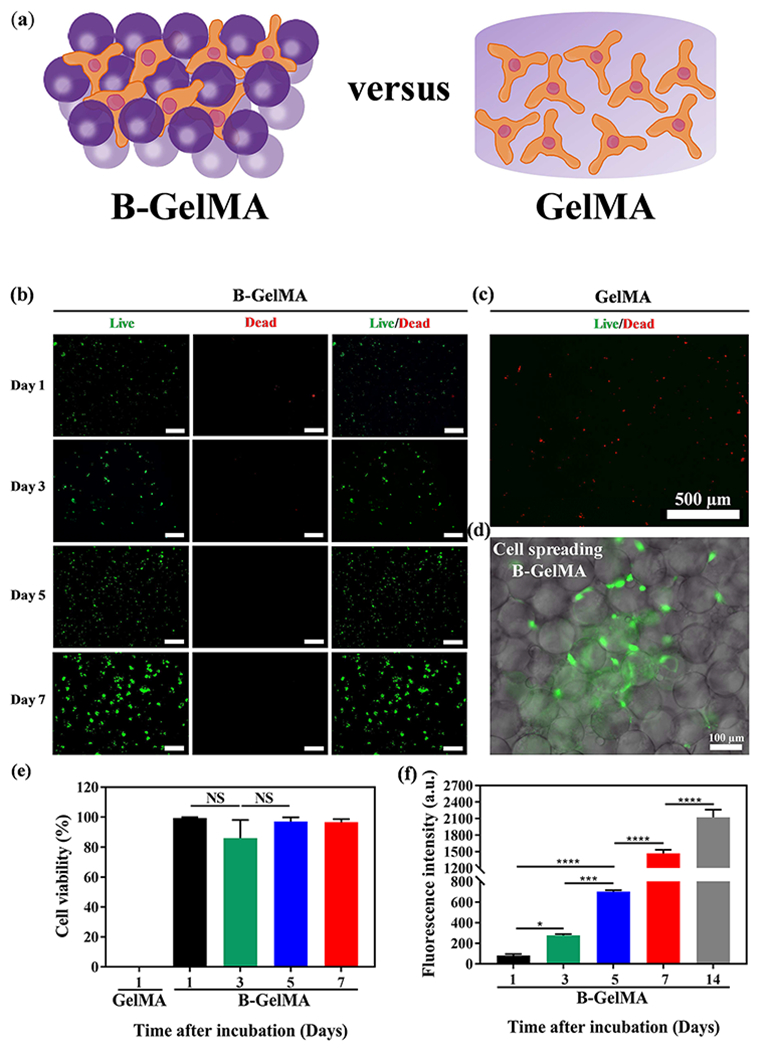
(a) Schematic of 3D cell culture in B-GelMA versus bulk GelMA. (b) Assessment of live (green) and dead (red) cells, showing that the 3D encapsulation of NIH/3T3 fibroblasts in B-GelMA scaffolds with a high polymer concentration (20% w/v) results in high cell viability, excellent adhesion, and significant proliferation, compared to the bulk GelMA (c) in which cells do not survive the first day of culture. Scale bars are 500 μm. (d) Fluorescent microscopy image of cells adhering to the annealed GelMA beads and spreading among them. (e) Cell viability, defined as the number of live cells divided by the total cell number for GelMA and B-GelMA, showing that while GelMA do not support cells, B-GelMA yields ~ 100% viability within an extended time. (f) Metabolic activity of the cells, measured using the PrestoBlue® assay, showing that B-GelMA affords an ~ 25-fold increase in the metabolic activity (proliferation) within 14 days. No metabolic activity was observed in the bulk GelMA.
