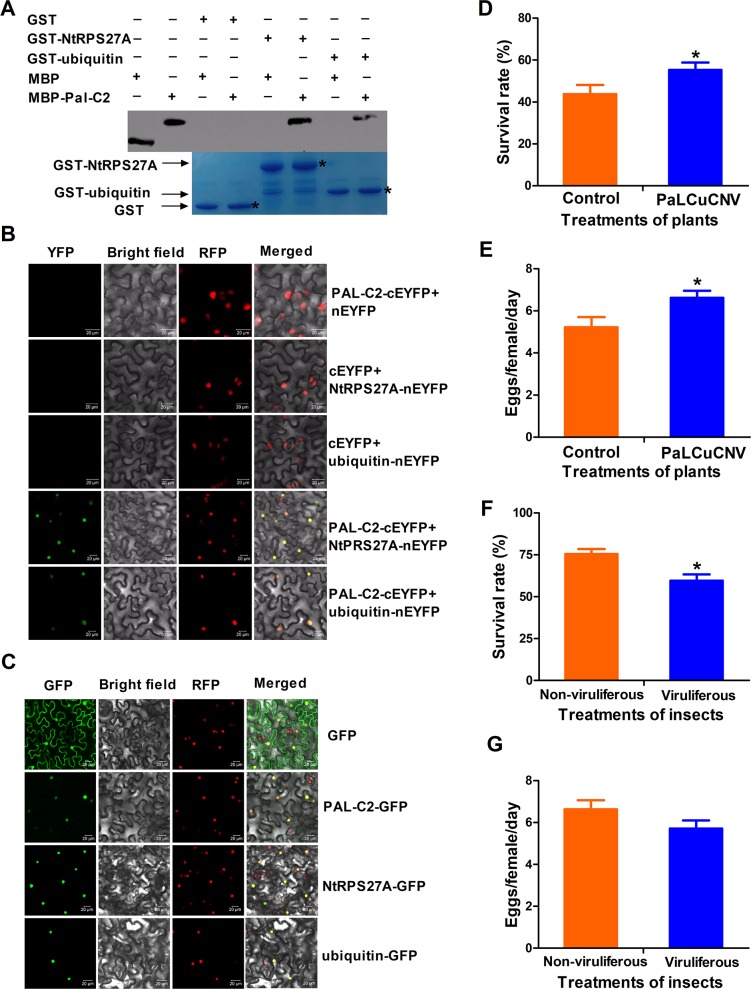
Fig 5. PaLCuCNV C2 interacts with RPS27A and promotes the performance of whitefly.
(A) In vitro GST pull-down assays. MBP or MBP-PaL-C2 fusion proteins were pull-down by GST or GST-NtRPS27A fusion protein. GST beads were washed and proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE western blot. Associated proteins were detected by anti-MBP antibody and gels were stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue to monitor GST and GST fusion proteins. (B) In vivo BiFC analysis of PaL-C2 interaction with NtRPS27A or ubiquitin. Nuclei of tobacco leaf epidermal cells were marked with a RFP fusion protein which is located in nucleus. Bars = 20 mm. (C) Subcellular localization of PaL-C2, NtRPS27A and ubiquitin. Nuclei of tobacco leaf epidermal cells were marked with a RFP fusion protein. Bars = 20 mm. (D) Survival rate of adult whitefly on control and PaLCuCNV-infected tobacco plants. Values are means±SE, n = 30. (E) Daily number of eggs laid by per female whitefly on control empty-vector-inoculated and PaLCuCNV -infected tobacco plants. Values are means±SE, n = 30. (F) Survival rate of non-viruliferous and viruliferous adult whiteflies on cotton plants. Values are means±SE, n = 30. (G) Daily number of eggs laid by per non-viruliferous and viruliferous adult female whiteflies on cotton plants. Values are means±SE, n = 30. Asterisks indicate significant differences between different treatments (P < 0.05; Student’s t test for all experiments). All experiments were repeated three times with similar results.