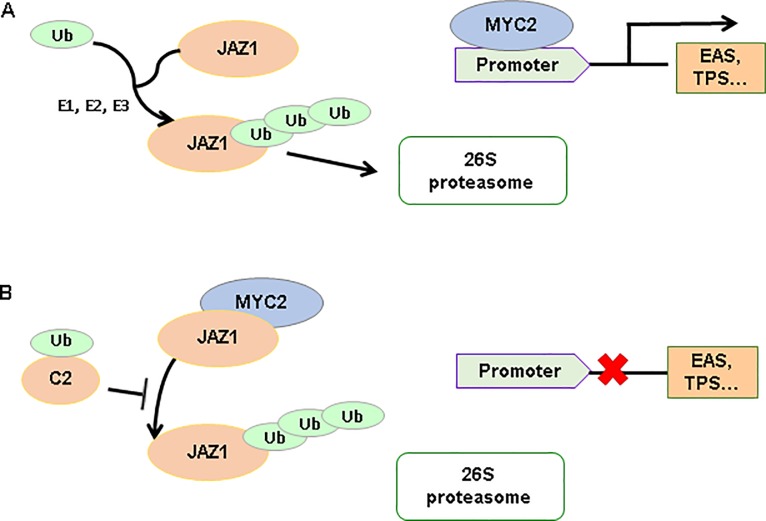
Fig 7. Model for the role of TYLCV C2 in regulating plant defense.
(A) When plants are infested by whiteflies, JAZ1 protein can be degraded by ubiquitination via El ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2) and E3 ubiquitin–protein ligase (E3) in 26S proteasomes. Then the MYC2 transcription factor is released from JAZ1-MYC2 protein complex, binds to the promoter of defense genes and activates the expression of down-stream defense genes, such as epi-arisotolchene synthase (EAS), and terpene synthase (TPS). As a consequence, plant defense is triggered. (B) When TYLCV and whitefly co-infect plants, TYLCV C2 protein competitively bind to ubiquitin, which lead to the decrease of JAZ1 protein ubiquitination. As a consequence, the MYC2 is bound to JAZ1 and unable to induce the gene expression of down-stream defense genes.