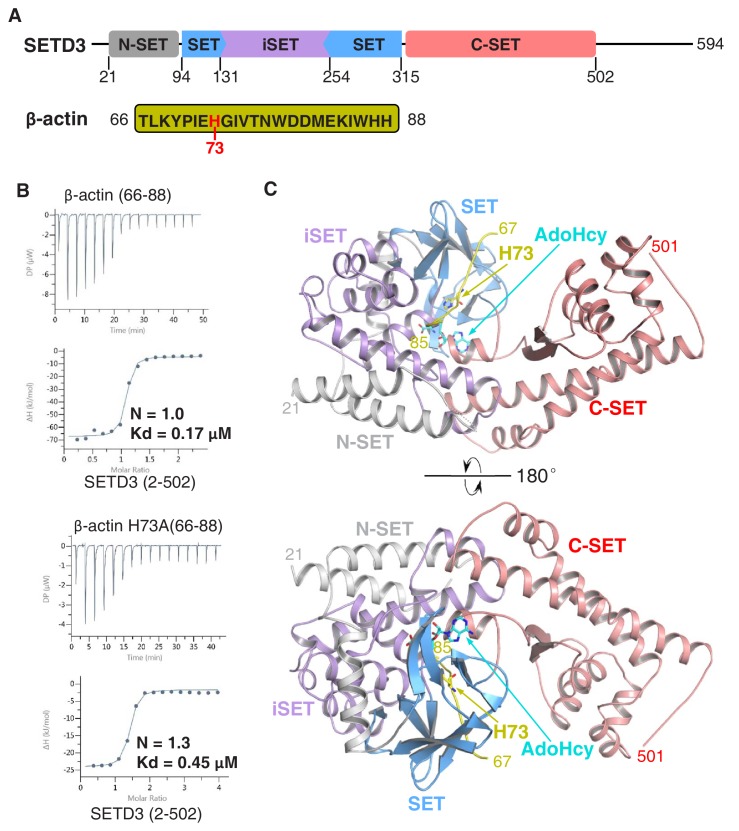
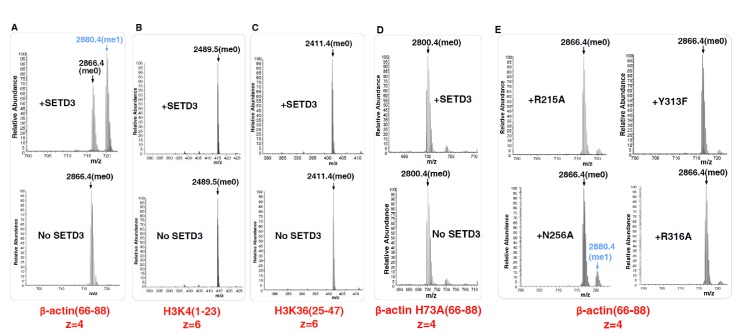
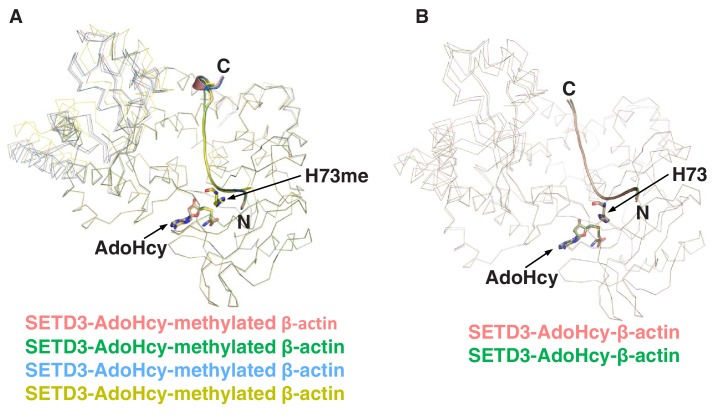
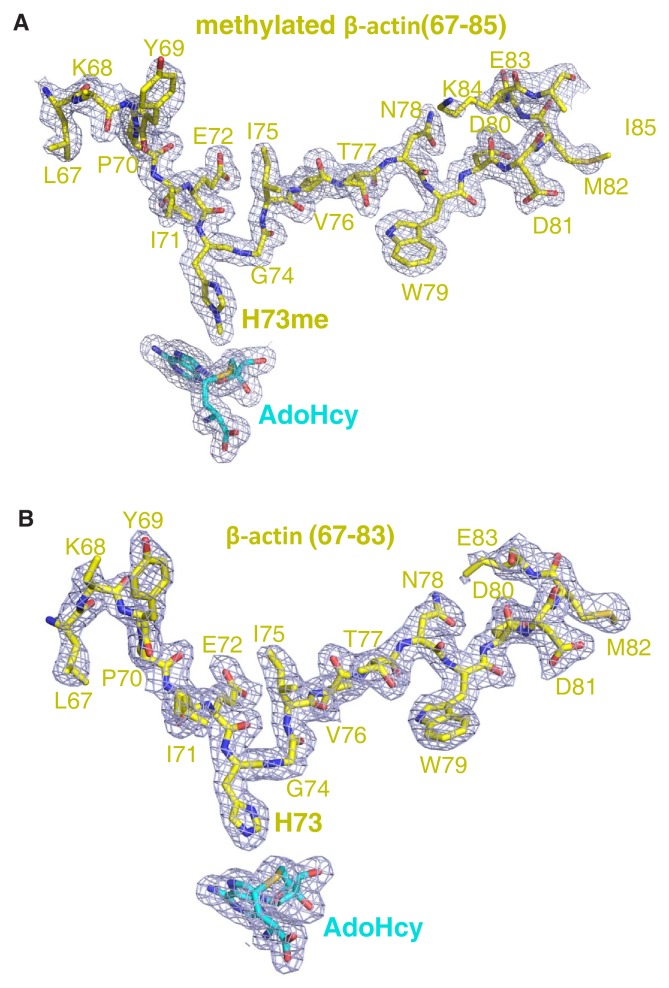
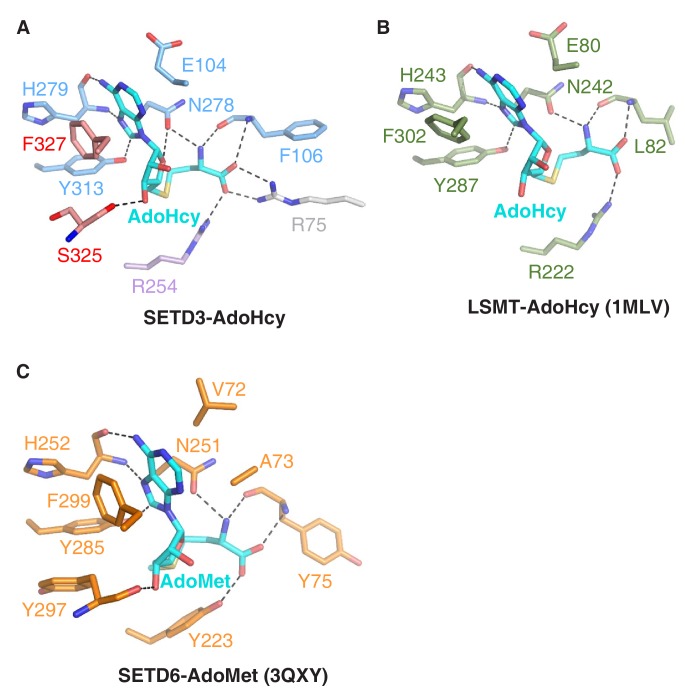
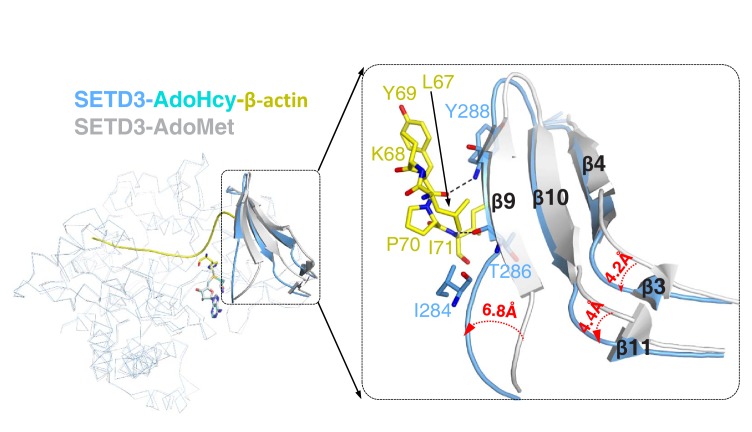
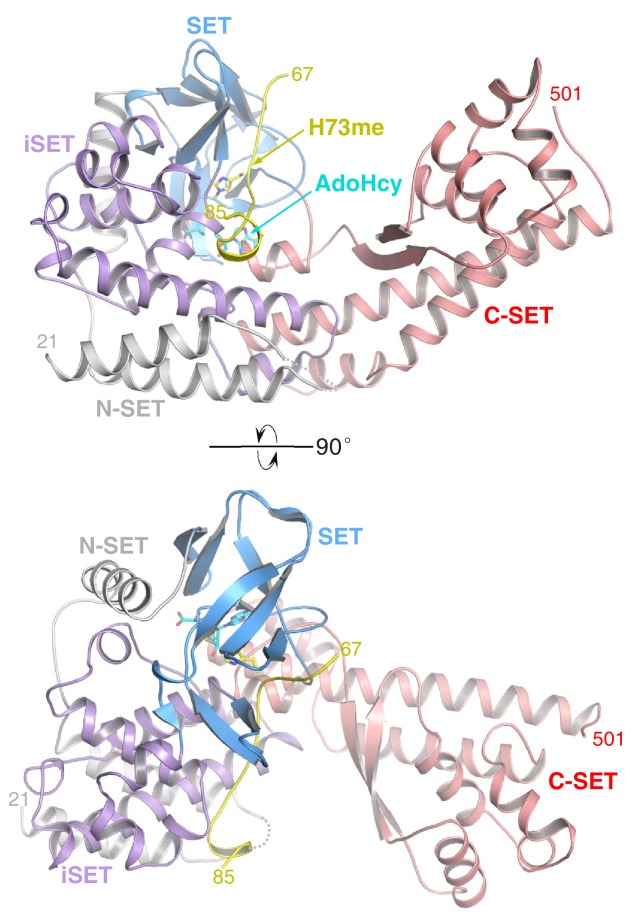
Figure 1. The SETD3 core region specifically recognizes a fragment of β-actin containing His73.
(A) Domain architecture of full-length human SETD3 (aa 1–594) and the sequence of the β-actin peptide (66–88), with His73 of β-actin highlighted. (B) Representative ITC binding curves for the binding of SETD3 (aa 2–502) to β-actin peptides of different lengths. The molecular ratios, derived Kds and respective standard deviations are also indicated. (C) The overall structure of AdoHcy-bound SETD3 with unmodified β-actin peptide. The SETD3 domains are colored in the same way as in Figure 1A, with the N-SET, SET, iSET and C-SET regions of SETD3 colored in gray, blue, purple and pink, respectively. The peptide is shown in yellow cartoon, while His73 and AdoHcy are shown in yellow and cyan sticks, respectively. His73 of actin and the AdoHcy are labeled.