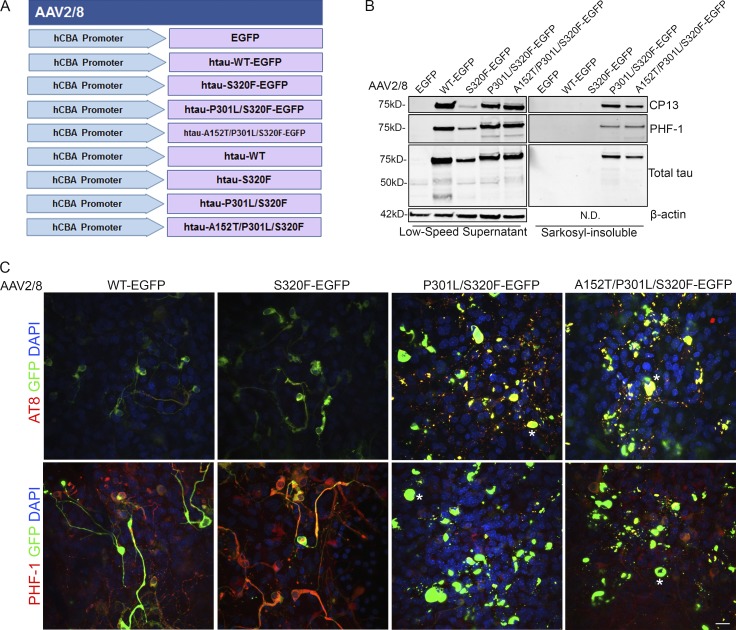
Figure 3.
rAAV tau-EGFP fusion protein transduced BSCs develop highly phosphorylated and sarkosyl-insoluble tau inclusions. (A) Schematic diagram of rAAV human mutant and WT tau constructs under a hCBA promoter used to transduce organotypic BSCs. Slice cultures were prepared and transduced with rAAV2/8-EGFP, rAAV2/8-WT-htau-EGFP, rAAV2/8-S320F-htau-EGFP, rAAV2/8-P301L/S320F-htau-EGFP, or rAAV2/8-A152T/P301L/S320F-htau-EGFP (1–2 × 1010 VGs per well) at 0 DIV and then maintained in culture until 28 DIV. (B) Transduced slices were sequentially extracted in order to prepare sarkosyl-insoluble tau fractions, and then lysates were immunoblotted for tau phosphorylated at Ser202 (CP13), tau phosphorylated at Ser396/404 (PHF-1), total tau (3026), and β-actin as a loading control. Representative Western blots of tau in the low speed supernatant and sarkosyl-insoluble fraction are shown. n = 9. (C) Transduced slice cultures were fixed, immunostained for tau phosphorylated at Ser396/Ser404 (PHF-1) and tau phosphorylated at Ser202/Thr205 (AT8), and confocal imaged to identify the location of phosphorylated tau in these sections. Asterisks mark examples of cells showing somatodendritic accumulation of phosphorylated tau. Bar, 25 µm. n = 3.