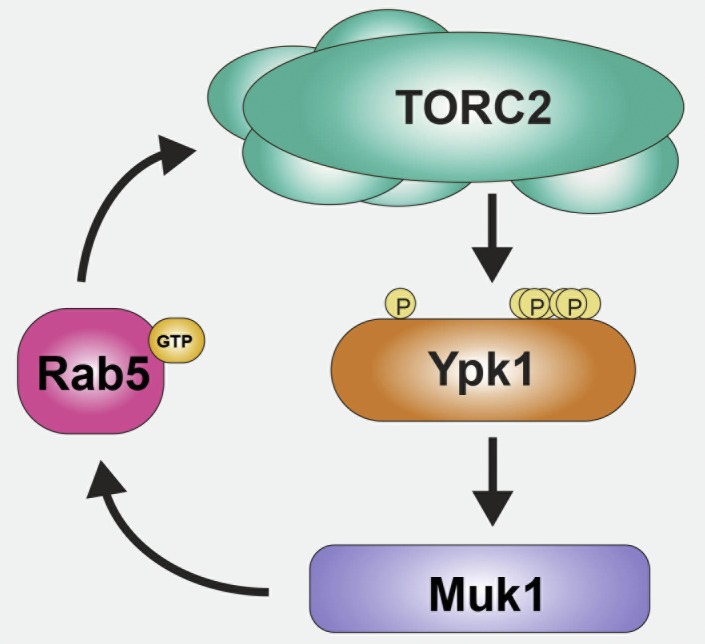
Figure 7.
Muk1-dependent Rab5-mediated mechanism for sustained activation of TORC2-Ypk1 signaling. Basal Ypk1 (orange) activity requires phosphorylation of T504 in its activation loop (indicated by the left-most P) and TORC2-mediated phosphorylation at S644 near its C terminus. However, under many stress conditions, TORC2 (aqua) up-regulates Ypk1 by phosphorylating T662 and additional multiple sites at its C-terminal end (indicated by the cluster of Ps to the right). As documented in this study, activated Ypk1 phosphorylates the Rab5-specific GEF Muk1 (purple), which in turn is activated by its Ypk1-mediated phosphorylation. Activated Muk1 will generate more GTP-bound Rab5 (pink), and as we also have demonstrated here, activated Rab5 promotes the ability of TORC2 to phosphorylate Ypk1. Based on the observed coimmunoprecipitation of the Rab5 Vps21 with the Tor2 catalytic subunit of TORC2, the stimulation of TORC by Rab5 may be direct.