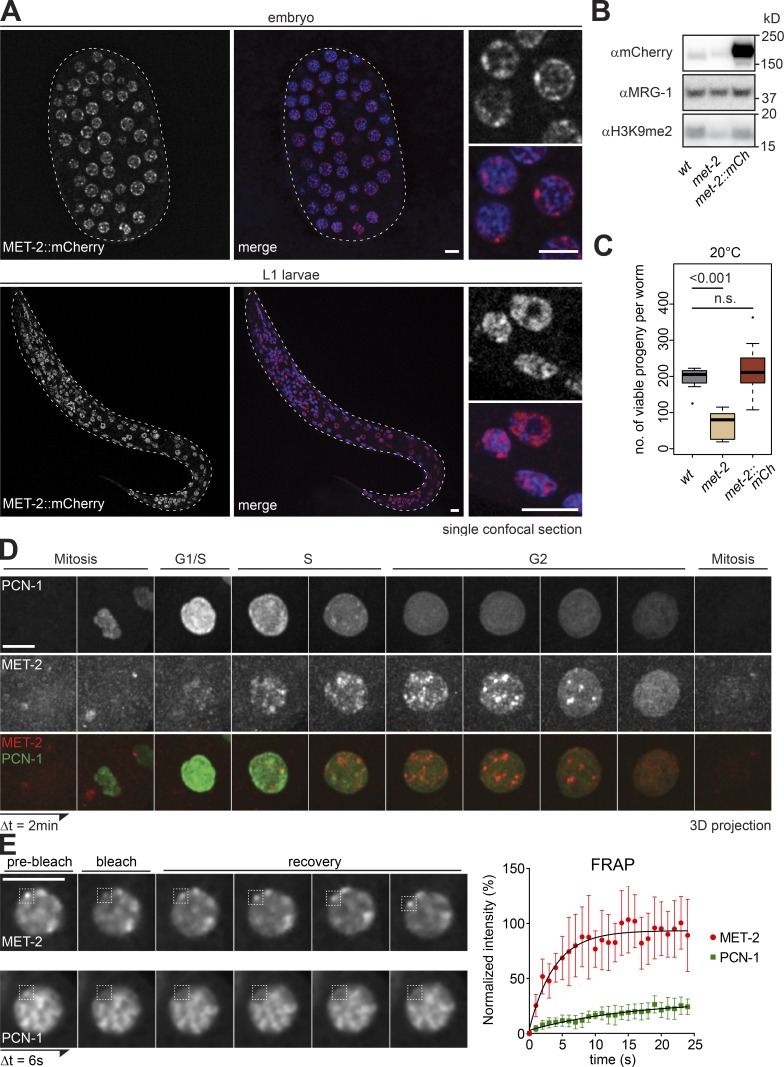
Figure 1.
A functional MET-2::mCh fusion forms nuclear foci through C. elegans development. (A) Confocal sections of MET-2::FLAG::mCherry (red) and Hoechst (blue) in a pregastrulation C. elegans embryo and L1 stage larva. Bar = 5 µm. (B) Western blot of whole-cell lysates of wild-type (N2), met-2(n4256), and met-2::flag::mcherry(gw1419) embryos blotted for H3K9me2, mCherry, and MRG-1 as a control (quantified in Fig. S1 B). (C) Number of viable progeny of strains used in B cultured at 20°C (N = 2, n = 50; P values calculated using two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test). (D) Representative Z-projected images from time-lapse series (2-min intervals) of early embryos, showing MET-2::FLAG::mCherry foci in S-G2 phase, identified by GFP::PCN-1. For movies, see Videos 1 and 2. Bar = 5 µm. (E) Left: Representative images of MET-2::FLAG::mCherry or GFP::PCN-1 FRAP over time. Interval between images, 6 s. Bar = 5 µm. Right: One representative experiment of three biological replicas is quantified. Error bars indicate 95% confidence interval. n = 9 and 12 nuclei, respectively.