Figure 1: Activation of Agrp neurons does not impair spatial learning.
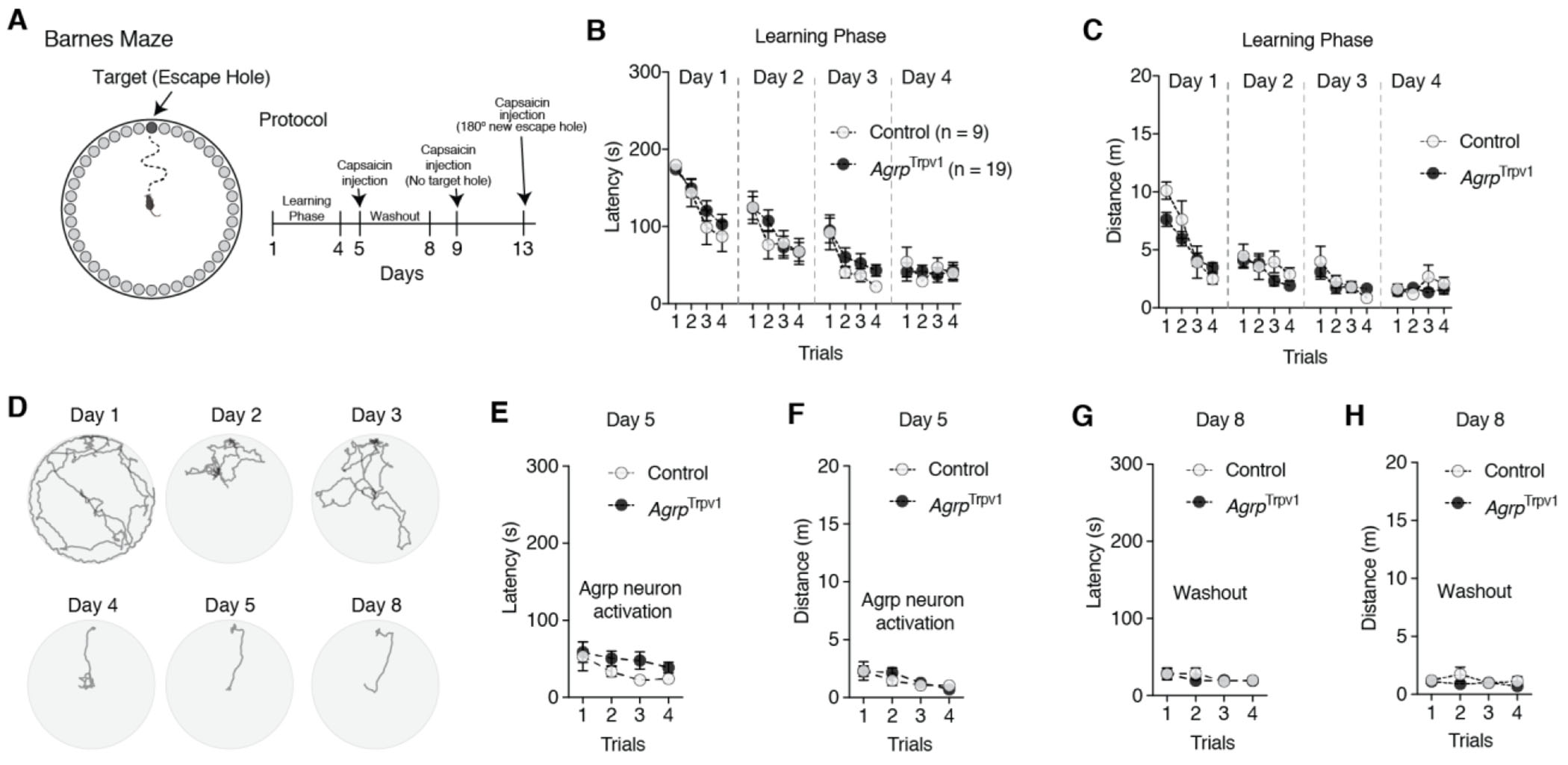
(A) Illustrative representation of Barnes Maze and experimental protocol. On days 5, 9, and 13 they received an injection of capsaicin (10 mg/kg, i.p.) before trials. Control (n = 9) and AgrpTrpv1 mice (n = 19) were tested. (B-C) Latency and distance traveled to reach the escape hole in the learning phase during trials across days. (D) Tracking data from a control animal representing one trial per day during the learning phase. (E-F) Latency and distance traveled to reach the escape hole upon Agrp neuron activation. (G-H) Latency and distance traveled to reach the escape hole three days after the injection of capsaicin, to probe the long-lasting effects of Agrp neuron activation. In B, C, E, F, G, and H symbols represent mean ± SEM. Statistically significant P values are provided in the panels.
