Fig. 6.
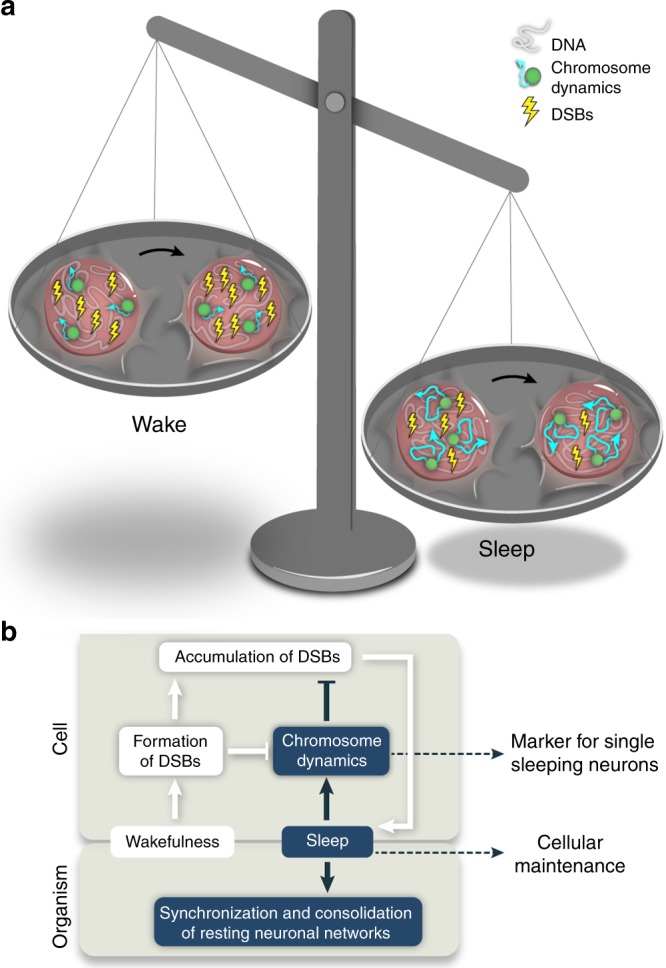
A proposed function for sleep. a During wakefulness, chromosome dynamics are low and the number of DSBs is accumulated in neurons. The beneficial role of sleep is to increase the chromosome dynamics that are essential for the efficient reduction of the number of DSBs in single neurons. b DSBs are increased in the nucleus during wakefulness and are formed by intrinsic and extrinsic factors, such as neuronal activity, irradiation, and oxidative stress, when chromosome dynamics are low. At a given threshold, accumulations of DSBs in multiple neuronal networks can trigger sleep, which increases chromosome dynamics that are necessary for the reduction of DNA damage. This mechanism suggests that chromosome dynamics can define single sleeping neurons, and that one of the functions of sleep is nuclear maintenance
