Figure 1.
Intestinal DMT1 Is Required for Vectorial Iron Flux across the Duodenal Epithelium during IDA
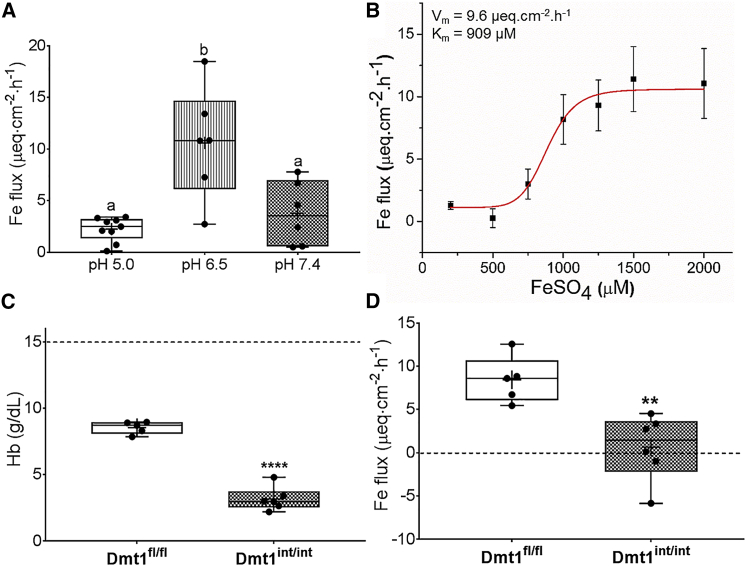
Duodenal epithelial sheets isolated from adult male WT mice were used initially to determine the optimal conditions for assessing iron flux in the Ussing chamber and then to define kinetic parameters of iron transport. Iron flux was then assessed in anemic adult Dmt1fl/fl and Dmt1int/int mice. Shown is iron (59Fe) flux at pH 5.0. 6.5, and 7.4 in WT mice in the presence of 1,000 μM FeSO4 (n = 6–9 mice/pH group) (A). Iron flux at different iron concentrations (at pH 6.5) in WT mice (n = 3–5 at each iron concentration) was subsequently measured (B), and kinetic parameters were calculated (see values in the upper left corner). Serum Hb concentrations in Dmt1fl/fl mice with facial vein bleeding and untreated Dmt1int/int mice are also shown (n = 5–6/group) (C). The dashed line indicates the approximate Hb concentration in untreated Dmt1fl/fl mice (for comparison). Iron flux was assessed in duodenal sheets isolated from these mice in the presence of 1,500 μM FeSO4 at pH 6.5 (n = 5–6 per group) (D). p = 0.345 for Fe flux being >0 in Dmt1int/int mice. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA (A) or t tests (C and D) and are presented as boxplots. Groups labeled with different letters are different from one another: (p = 0.0005) (A); ****p < 0.0001 (C); **p < 0.01 (D).