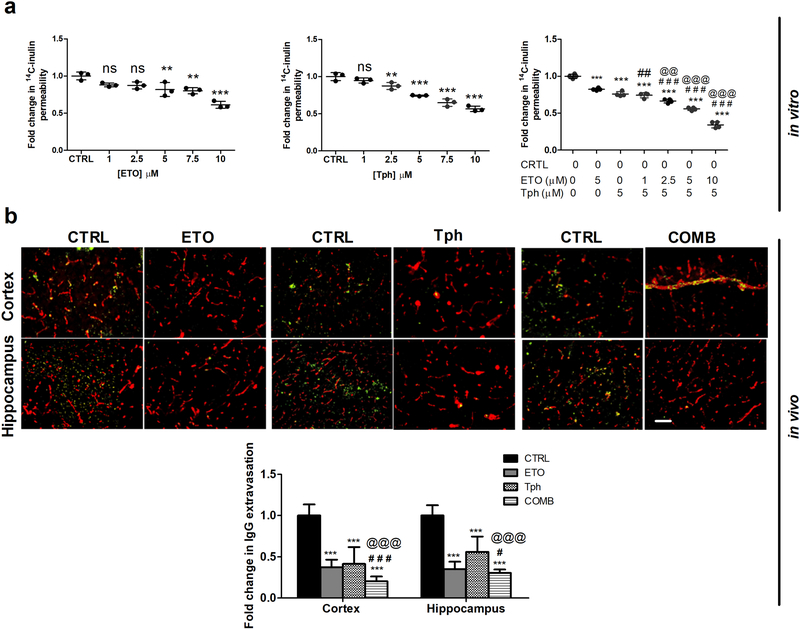
Figure 1.
Combination (COMB) treatment significantly enhanced BBB intactness compared to vehicle (control = CTRL), and etodolac (ETO) and/or α-tocopherol (Tph) treated groups.
(a) In vitro concentration-dependent effect of ETO, Tph, and COMB on permeation of the paracellular permeability marker 14C-inulin across a bEnd3 cell-based BBB model. Data represented as mean ± SD of 3–4 independent experiments with n=4 wells/treatment/experiment. (b) Representative brain sections of 5XFAD mice treated with ETO, Tph, and COMB stained with anti-IgG to quantify endogenous IgG extravasation (green) and anti-collagen antibody to resolve microvessels (red) in cortex and hippocampus regions with quantitative analysis of IgG optical density. Scale bar, 50 μm. Data represented as mean ± SEM of n=5 mice per treatment and n=9 mice for control group. ns = not significant; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to CTRL; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001represent COMB compared to ETO alone; @@ p < 0.01, @@@ p < 0.001represent COMB compared to Tph alone.