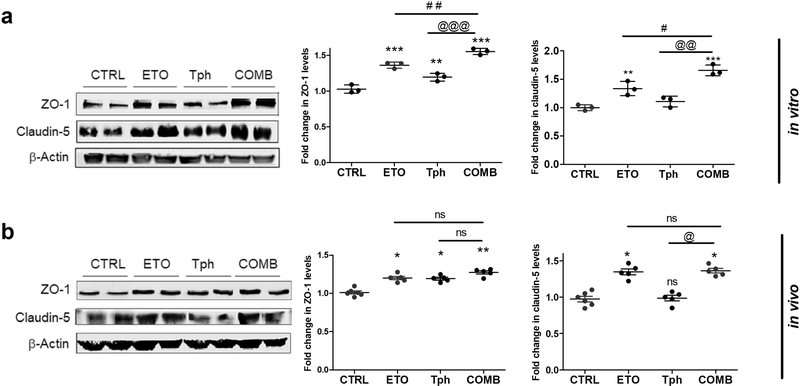
Figure 2.
Combination (COMB) treatment significantly increased tight junction proteins expression in vitro in bEnd3 cells and in vivo in isolated mice brain microvessels compared to vehicle treated groups (control = CTRL), and etodolac (ETO) and/or α-tocopherol (Tph).
(a) Representative Western blot and densitometry analysis of ZO-1 and claudin-5 expression in bEnd3 cells. Cells were treated with 10μM of each compound for 24 h. Data represented as mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments with n=3 dishes/treatment/experiment. (b) Representative Western blot and densitometry analysis of ZO-1 and claudin-5 in vivo from microvessels isolated from 5XFAD mice brains. Microvessels were isolated from the homogenate of the right hemisphere of mice brains (n=5–6 mice). Mice were treated with ETO, Tph or COMB at 10 mg/kg/day each for 30 days. Data represented as mean ± SEM of n=5–6 mice per group. ns = not significant; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to CTRL; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 represent COMB compared to ETO alone; @ p < 0.05, @@ p < 0.01, @@@ p < 0.001represent COMB compared to Tph alone.