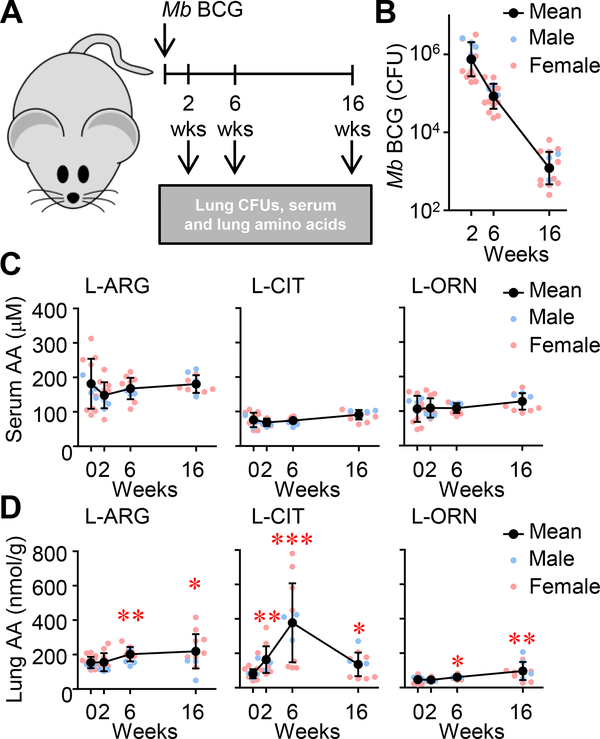
Figure 1. Metabolites of L-ARG metabolism in the lung and serum following pulmonary M. bovis BCG infection.
(A) Male and female C57BL/6 mice were infected with M. bovis BCG via intranasal inoculation. (B) At 2, 6, and 16 weeks post-infection, CFUs were determined from lung homogenates (N=16, 3 experiments combined). (C, D) Concentrations of L-ARG, L-CIT, and L-ORN in the serum (C) and lung homogenates (relative to lung mass) (D) were determined by LC-MS/MS. (N=12, 2 experiments combined). Data are the individual CFUs or amino acid concentrations (Male = blue, Female = pink), with the mean represented by black symbols. Error bars, SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by Student’s t test comparing indicated data to uninfected mice (i.e. 0 weeks).