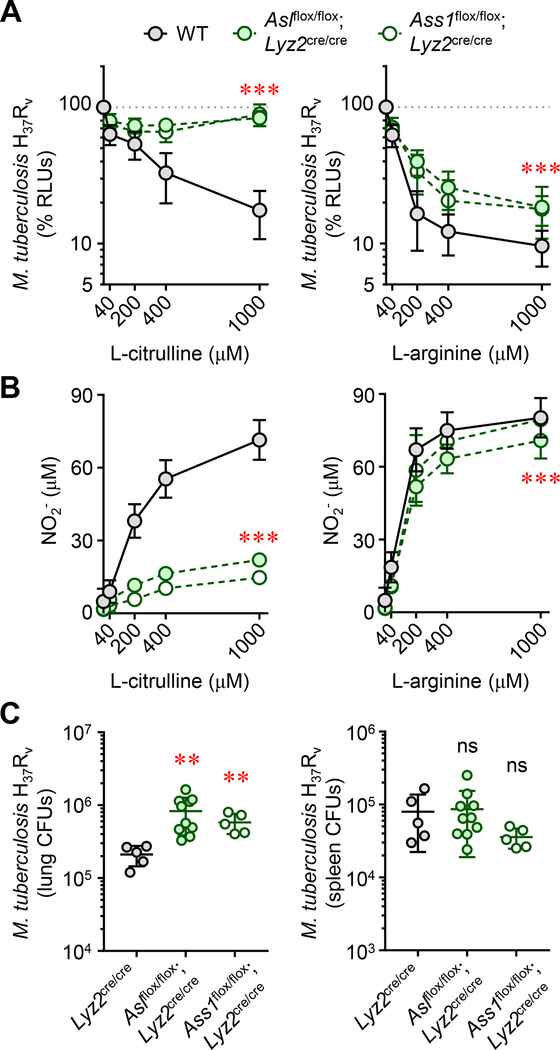
Figure 4. Myeloid-specific L-ARG synthesis is necessary for host defense against virulent M. tuberculosis.
(A and B) Thioglycollate-elicited peritoneal-derived macrophages (PDMs) collected from As1flox/flox;Lyz2cre/cre, Ass1flox/flox;Lyz2cre/cre, or control mice (N≥8), cultured in titrating L-CIT or L-ARG, were stimulated with IFN-γ and infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv. M. tuberculosis viability was determined by RLU at 72 hours post-infection (A). Data are the mean percent RLUs (RLUs from cultures without L-CIT or L-ARG were set to 100%). Nitric oxide production was determined by measuring NO2- at 72 hours post infection (B). For (A) and (B), the y-axis intersects the x-axis at “0”. (C) Male and female As1flox/flox;Lyz2cre/cre (N=10), Ass1flox/flox;Lyz2cre/cre (N=5), or Lyz2cre/cre (N=5) control mice were infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv via intranasal inoculation. Eight weeks post-infection, mice were euthanized and the lung and spleen were analyzed by CFU enumeration. Data are presented as a scatter plot of individual CFU values with the line representing the mean. Error bars, SD. Data are combined from at least two experiments (A, B) or are from one of two independent experiments (C). ***p < 0.001 comparing either As1flox/flox;Lyz2cre/cre or Ass1flox/flox;Lyz2cre/cre to WT by 2-way ANOVA (A and B); **p < 0.01, comparing indicated data to Lyz2cre/cre WT controls by Student’s t test (C).table