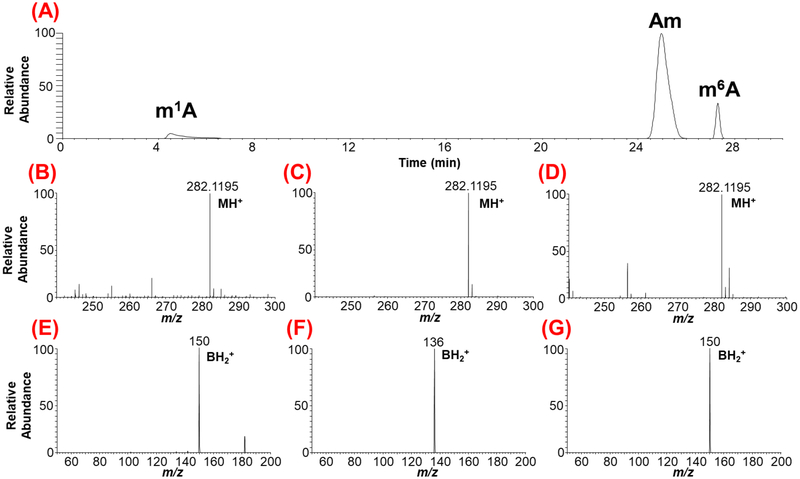
Figure 3:
LC-MS/MS-based characterization of the methylated positional isomers of adenosine originating from yeast mRNA. (A) Extracted ion chromatogram (XIC) for m/z 282.1195 corresponding to methylated adenosine is shown. The methylated positional isomers exhibit different retention times depending on their hydrophobicity. (B), (C), (D), depict the mass spectra of chromatographic peaks with retention times at 4.8, 25.8 and 27.5 min, respectively. (E), (F), (G) represent the tandem mass spectra showing the nucleobase ion of molecular precursor ion for a given XIC. Note the differentiation of ribose methylated adenosine (Am) from base methylations (m1A and m6A) through nitrogenous base productc ion. However, the tandem mass spectra for base methylations, (E) and (G) do not distinguish the position of methylation on nitrogenous base as both exhibit identical nucleobase product ion.