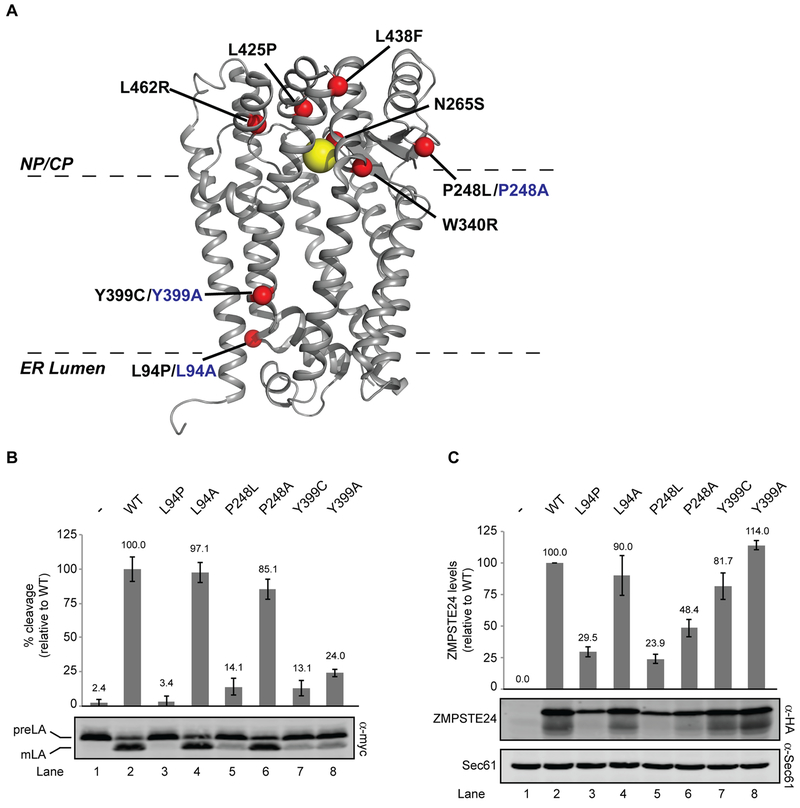
Figure 4. Structure-function studies of ZMPSTE24.
(A) X-ray crystal structure of human ZMPSTE24 (PDB entry 2ypt) with zinc indicated by the yellow ball and disease residues indicated with red balls. Disease alleles are labeled in black, with alanine changes in blue. The predicted placement of ZMPSTE24 in the membrane bilayer is shown (B). SM6158 (ste24Δ 10His-3myc-LMNACT) transformed with the indicated ZMPSTE24 mutants were analyzed by western blotting to determine prelamin A cleavage activity, which was calculated as a ratio of mature lamin A to total myc signal (prelamin A + mature lamin A), as described in Methods section. Average cleavage and standard deviation of the mean for three independent experiments is shown, with wild-type ZMPSTE24 activity set to 100% for comparison. (C) ZMPSTE24 protein levels were analyzed by western blotting using anti-HA (normalized to the loading control Sec61). The average and standard deviation of the mean is shown for the same three experiments as in (B). Wild-type ZMPSTE24 protein levels are set to 100% for comparison.