Figure 3. Despite higher pVHL HIF-1α accumulates in nuclear extract of MEK2 deficient BMDMs and co-immunoprecipitates with p300/CBP.
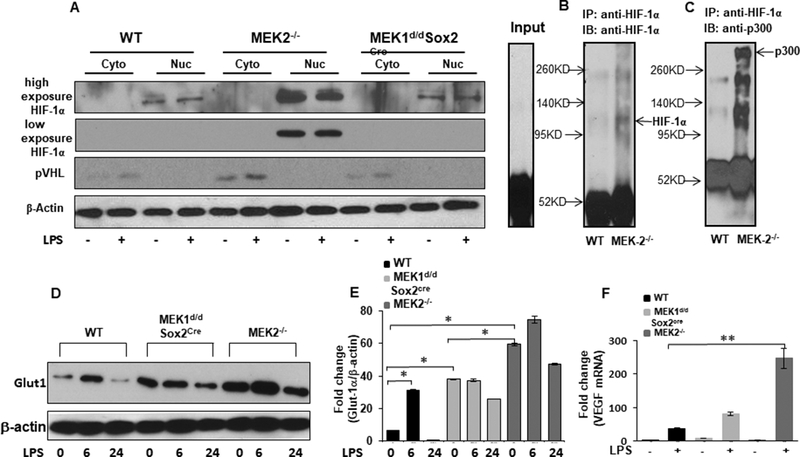
WT, MEK2−/−, and MEK1d/dSox2cre BMDMs were cultured and challenged with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 3h. Nuclear and cytosolic extracts were prepared and subjected to SDS-PAGE. (A) Western blot analysis was performed using specific antibodies against, VHL, HIF-1α and against β-actin. MEK2−/− BMDMs exhibit higher HIF-1α in nuclear extracts. Protein lysates prepared from untreated WT and MEK2−/− BMDMs were immunoprecipitated with HIF-1α specific antibody and equal amount of immunoprecipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE. (Band C) Western blot analysis was performed using specific antibodies to HIF-1α and p300/CBP. MEK2−/− BMDMs exhibit higher p300/CBP protein in the lysates immunoprecipitated with HIF-1α specific antibody. (D) GLUT1 expression. BMDMs derived from WT and MEK2−/− and Mek1d/d Sox2Cre mice were treated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 6 h and 24h. Whole cell extracts were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis using specific antibody against GLUT1. Equal loading was determined using antibody against β-actin. (E) Densitometric analysis of at least 3 independent experiments expressed as fold change of the ratio Glut1/ β-actin. MEK2 deficiency exhibited higher Glut1 levels in response to LPS. (F) VEGF mRNA expression. Total RNA was extracted from WT and MEK2−/− and Mek1d/d Sox2Cre BMDMs treated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 1h and VEGF expression was assessed using qRT-PCR. Values were normalized to GAPDH. Results represent mean values of 4 independent experiments. Using ANOVA Mann-Whitney U test, * signifies a p value <0.05, while ** signifies a p value <0.001, and error bars indicate SEM. MEK2 deficient BMDMs showed highly significant expression of VEGF in response to LPS.
