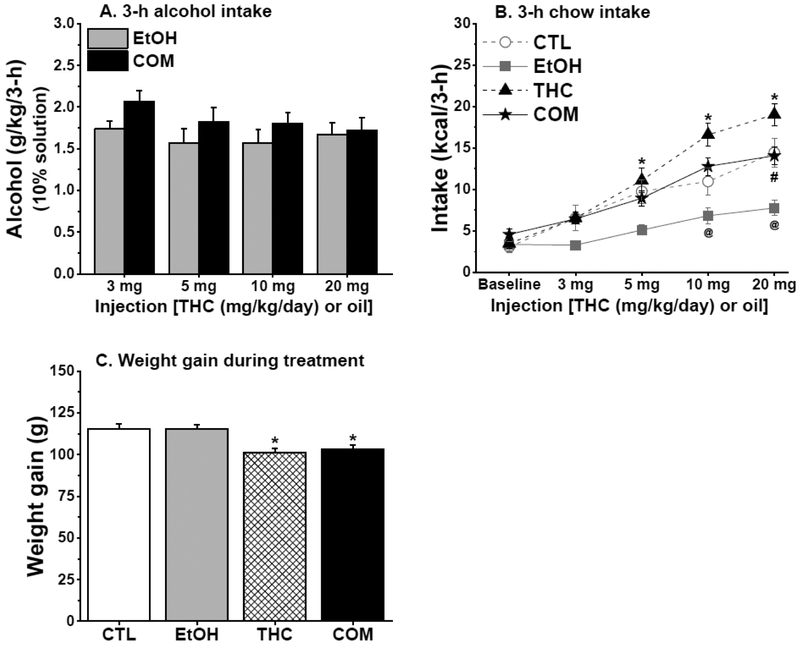
Fig. 5.
Chronic subcutaneous THC and voluntary alcohol consumption, alone or when combined, differently affected caloric intake and weight gain (Experiment 1b: n = 10/group). (A) EtOH & COM rats consumed similar doses of sweetened 10% alcohol solution. (B) THC injection dose-dependently increased 3-h chow intake only in the COM relative to the EtOH group. Alcohol consumption reduced 3-h chow intake, but THC averted the hypophagic effect of alcohol. THC vs. EtOH: *p < 0.05; EtOH vs. COM: @p < 0.05; CTL vs. EtOH: #p < 0.02. (C) Subcutaneous THC suppressed weight gain in the THC & COM groups. THC or COM vs. CTL or EtOH: *p < 0.02.