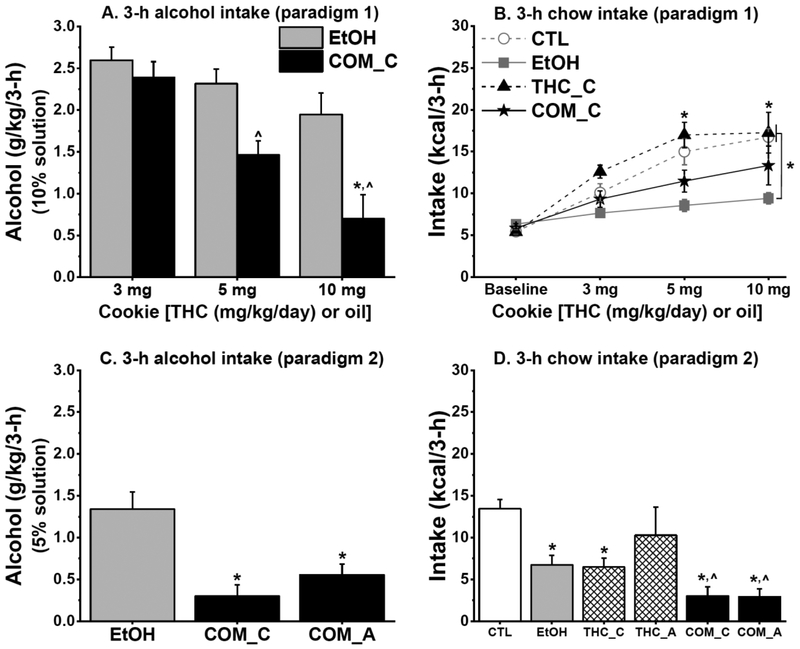
Fig. 6.
Chronic oral THC consumption reduced alcohol intake, while alcohol alone or when combined with oral THC reduced 3-h chow intake (Experiment 2a: CTL & EtOH, n = 8/group; THC_C, n = 5; THC_A, n = 3; COM_C & COM_A, n = 4). (A) In paradigm 1 (P30–39), COM_C rats consumed lower doses of sweetened 10% alcohol solution than did EtOH rats: *p < 0.009. COM_C rats also consumed reduced alcohol doses during 5 & 10 mg/kg/day THC consumption than they did during 3 mg/kg/day THC consumption: ^p < 0.03. (B) Moderate 10% alcohol consumption suppressed 3-h chow intake in EtOH rats. EtOH vs. CTL & THC_C: *p < 0.03. (C) When THC or oil cookie was consumed after sweetened 5% alcohol access in paradigm 2 (P40–45), COM_C & COM_A rats continued to consume less alcohol than the EtOH rats did. EtOH vs. COM_C & COM_A: *p < 0.05. (D) The EtOH, THC_C, COM_C, & COM_A groups consumed significantly lower 3-h chow compared with the CTLs. CTL vs. EtOH, THC_C, COM_C, & COM_A: *p < 0.008; THC_A vs. COM_C & COM_A: ^p = 0.055 & 0.050, respectively.