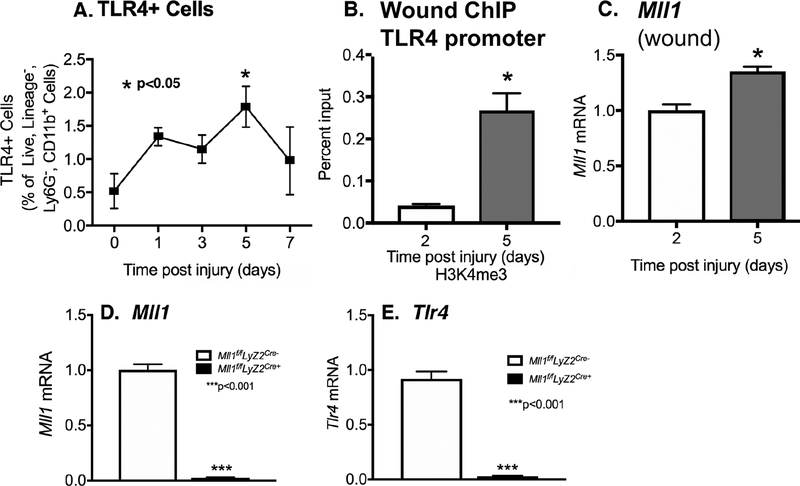
Figure 1. TLR4 and MLL1 is upregulated in myeloid cells in the early inflammatory phase of wound healing.
A: Wounds were created by 4-mm punch biopsy on C57BL/6 mice. Wounds were harvested on days 0, 1, 3, 5, and 7. Wound myeloid cells CD11b+[CD3−CD19−Ly6G−] were isolated and single cell suspensions were processed for flow cytometry with pseudocolor plots. Data analysis of TLR4+ cells as a percentage of live, lineage−, Ly6−, CD11b+ cells (n = 5). B: Wound myeloid cells were isolated at day 2 and 5 postinjury by MACS for CD11b+[CD3−CD19−Ly6G−] cells. ChIP analysis for H3K4me3 at TLR4 promoter on day 2 and day 5 in cells isolated from the wounds was performed (n = 15). For all ChIP experiments, isotype control antibody to IgG was run in parallel. C: Wound myeloid cells CD11b+[CD3−CD19−Ly6G−] were isolated and Mll1 expression was quantified using qPCR (n=10). D-E: Wound myeloid cells CD11b+[CD3−CD19−Ly6G−] were isolated from Mll1f/fLyz2Cre+ and Mll1f/fLyz2Cre- and Mll1 or Tlr4 expression was quantified using qPCR. Data are presented as the mean±SEM. Data are representative of 2–3 independent experiments. Data were first analyzed for normal distribution and if data passed normality test, 2-tailed Student t test was used.