Figure 2. Increase in TH and dopamine in differentiated mouse MN9D neuronal cells by aspirin.
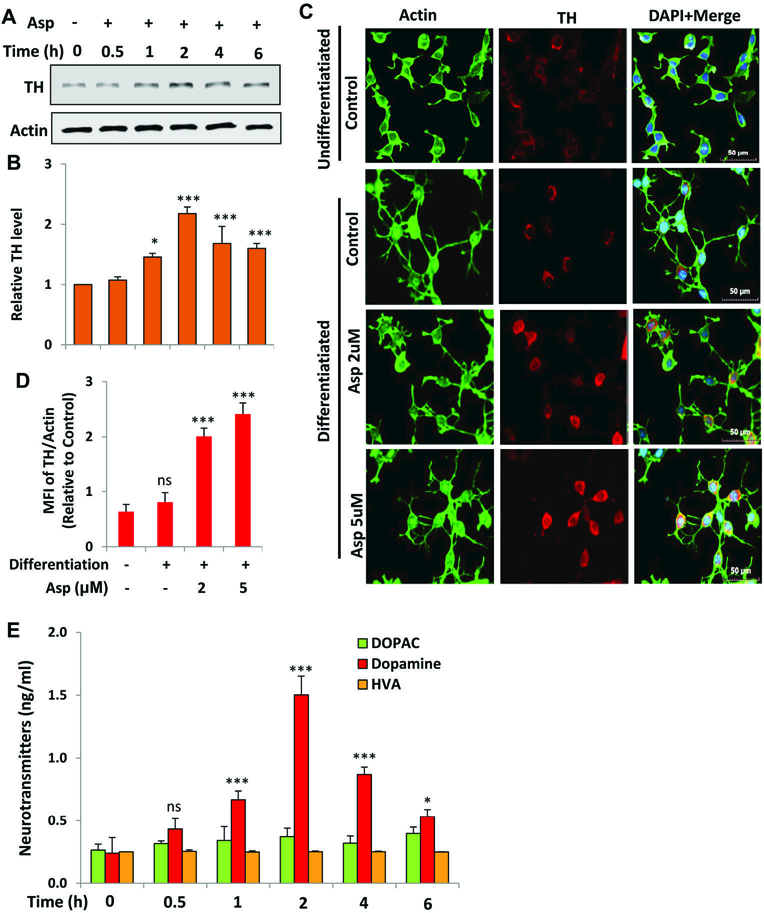
(A) Mouse MN9D neuronal cells were allowed to differentiate in neurobasal media containing B27 for 2 d following treatment with 2 μM aspirin for different time periods in neurobasal media without B27. The protein level of TH was monitored by Western blot (A). Bands were scanned and values (TH/actin) presented as relative to control (B). Results are mean SD of different experiments. *p < 0.05 & ***p < 0.001 vs control; ns, not significant. Cells were treated with 2 µM aspirin for 2 h followed by double-label immunofluorescence with antibodies against TH and actin (C). Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of TH and actin was calculated in 20 different cells (D) and presented as MFI-TH/MFI-actin. Results are mean ± SEM of 20 different cells per group. ***p < 0.001 vs control; ns, not significant. E) Cells were treated with 2 µM aspirin for different time periods followed by measuring the level of DA, DOPAC and HVA in supernatants by HPLC. Results are mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 & ***p < 0.001 vs control; ns, not significant. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test shows that time-dependent increase in DA by aspirin is significant (p < 0.0001).
