Figure 3. Oral administration of aspirin increases the level of TH in vivo in the nigra of C57/BL6 mice.
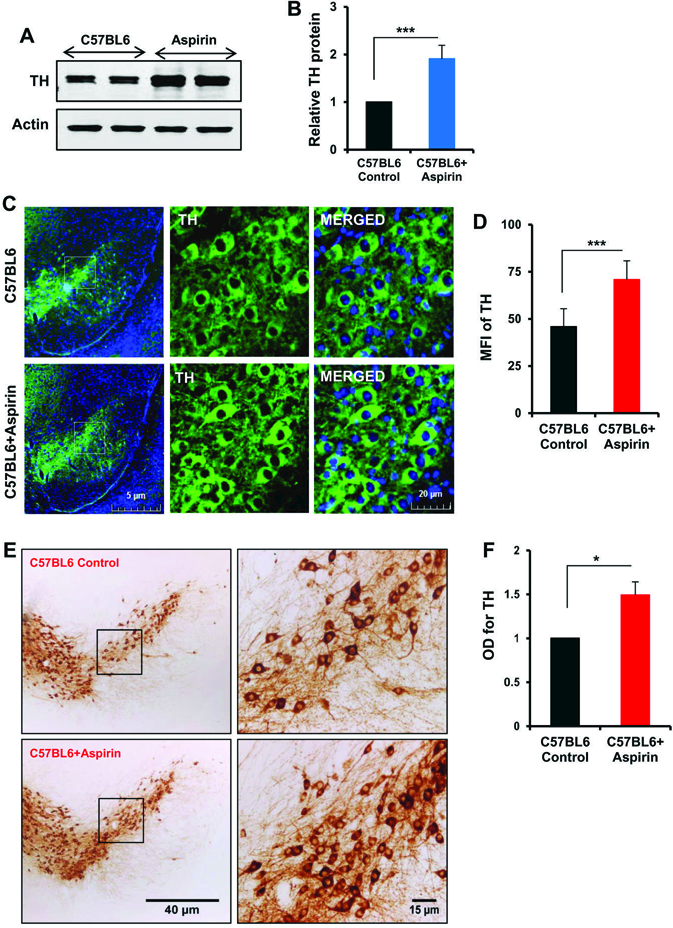
Male C57/BL6 mice (n=5 per group) were treated with aspirin (2 mg/kg body wt/d) mixed in 0.5% methylcellulose orally via gavage. Control mice received 0.5% methylcellulose as vehicle. After 30 d of treatment, the level of TH was monitored in the SNpc by Western blot (A). Actin was run as loading control. Bands were scanned and values (TH/actin) presented as relative to control (B). Results are mean + SEM of five mice per group. ***p<0.001 (= 5.28 × 10−4) vs control by two-tailed paired t-tests. The level of TH was monitored in ventral midbrain sections by immunofluorescence (C). MFI of TH (D) was calculated in two nigral sections of each of five mice per group. Results are mean ± SEM of five mice per group. ***p<0.001 (=1 × 10−7) vs control by two-tailed paired t-tests. The level of TH was monitored in ventral midbrain sections by DAB immunostaining (E). Optical density of TH (F) was calculated in two nigral sections of each of five mice per group. Results are mean ± SEM of five mice per group. *p<0.05 (= 0.012632) vs control by two-tailed paired t-tests.
